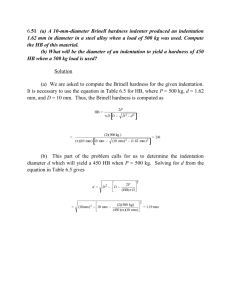
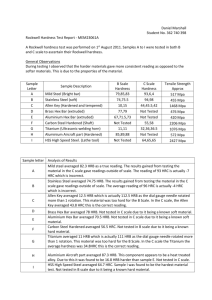
Mechanical Properties of Materials: Stress, Strain, Hardness
advertisement
บทที่ 5 สมบัตเิ ชิงกลของวัสดุ 1. ความเค้ น ความเค้ น (stress) คือ แรงกระทาในเนือ้ วัสดุต่อหนึ่งหน่ วยพืน้ ที่ ที่ตงั ้ ฉากหรือขนานกับแรงนัน้ มีหน่ วยเป็ น N/m2 หรื อ Pa หรื อ lb/in2 1 N/m2 = 1 Pa 1 lb/in2 = 6.89103 Pa Ex แท่ งอลูมิเนียม มีเส้ นผ่ านศูนย์ กลาง = 0.500 นิว้ ถูกแรง กระทา 2500 lb จงหาความเค้ นของแท่ งโลหะนี ้ จาก = 2500/ (/4)(0.5)2 = 12700 lb/m2 2. ความเครียด (Strain) ความเครียด () = ความยาวที่เปลี่ยนไป (l - lo) ความยาวเริ่มต้ น (lo) ดังนัน้ จึง ไม่ มีหน่ วย Ex : ชิน้ โลหะอลูมิเนียม กว้ าง 0.5 นิว้ หนา 0.04 นิว้ ยาว 8 นิว้ มีจุดกาหนด เกจช่ วงระยะ 2.00 นิว้ ที่จุดกึ่งกลาง เมื่อชิน้ งานถูกดึงที่ช่วงระยะเกจเปลี่ยนไป เป็ น 2.65 นิว้ จงหาความเครี ยด และเปอร์ เซ็นต์ ความยาวที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป 3. Poisson Ratio http://training.ce.washington.edu/WSDOT/Modules/03_materials/Images/Main%20Page%20Pictures/poisson.jpg Typical Values of Poisson’s Ratio Material Steel Aluminum PCC Flexible Pavement Asphalt Concrete Crushed Stone Soils (fine-grained) Poisson's Ratio 0.25 - 0.30 0.33 0.15 - 0.20* 0.35 (±) 0.40 (±) 0.45 (±) *Dynamic determination of µ could approach 0.25 for PCC (Neville, 1975) 4. Shear http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d0/Shear_scherung.svg/602pxShear_scherung.svg.png http://www.eng.uc.edu/~gbeaucag/RyanBreese/Rheolog/rheology_files/image001.jpg Tensile Testing การทดสอบแรงดึง เป็ นวิธีที่นิยมใช้ เพื่อวัดคุณสมบัติความต้ านทานของวัสดุต่อแรงที่มากระทา http://www.ssi.shimadzu.com/products/images/testing/iso527-tensile-image1.jpg http://www.mtec.or.th/labs/mech/tips7.html http://www.twi.co.uk/twiimages/jk69f4.gif http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6f/Al_tensile_test.jpg Stress vs. Strain curve typical of structural steel 1. Ultimate Strength 2. Yield Strength 3. Rupture 4. Strain hardeningregion 5. Necking region A: Apparent stress (F/A0) B: Actual stress (F/A) 1. Elastic modulus Elastic modulus : Hook’s law = E E = / E = Elastic modulus = Young’s modulus หน่ วย : psi / Pa 2. Yield strength กาลังวัสดุท่ จี ุดครากที่ 0.2% offset (proof strength/ offset yield strength) วัสดุเริ่มจะมีการแปรรู ปแบบถาวร (plastic deformation) 3. Ultimate strength เป็ นค่ ากาลังสูงสุดบนกราฟ ความเค้ น-ความเครียด 4. % Elongation L Lo 100% f (%El) = Lo 5. % Reduction Area A A o f 100% (%RA) = Ao http://www.auf.asn.au/const_images/stress_strain4.jpg The Bend Test for Brittle Materials Yield strength, Tensile strength, Breaking strength : are the same Flexural strength = modulus of rupture F = fracture load L = distance between the two outer point w = width of the specimen h = height of the specimen http://www.emeraldinsight.com/fig/0180570504001.png http://meetjoeblog.net/wp-content/uploads/2009/02/bending_test.jpg www.thefabricator.com/WeldingInspection/Weldi... www.aws.org/itrends/11-03/feature1.html การทดสอบความแข็ง (Hardness Test) การทดสอบความแข็งจะเกี่ยวข องกับการวัดความต านทานต อการเกิดเป นรอยกด โดยใช้ เครื่องมือที่เป็ น ลักษณะหัวกดที่มีหลายแบบ เช่ น แบบหัวบอล แบบระนาบ หรือแบบกรวยปลายมนหรือป รามิด ซึ่งปกติทาจากเหล็กกล า หรื อเพชรและใช้ ทดสอบภายใต้ สภาวะนา้ หนักคงที่โดย การวัดนา้ หนักที่จะทาให เกิดรอยกดตามที่กาหนดหรื อวัด รอยกดที่เกิดขึน้ ภายใต แรงกระทานัน้ การทดสอบความแข็งกับวัสดุโลหะส วนใหญ เป นการ ทดสอบแบบ Brinell หรือ Rockwell ส วนการทดสอบแบบอื่นคือการทดสอบแบบ Shore , Vickers, Rockwell superficial และเครื่องทดสอบ Herbert จะใช ในการทดสอบโลหะที่มีความแข็งแรงสูง หรือ เหล็กกล้ าที่ผ านการชุบผิวนอกจากนัน้ ในการทดสอบความแข็ง บางครัง้ ต องทาการทดสอบกับวัสดุท่ เี ล็กและบางมาก หรือวัสดุท่ มี ีระดับความแข็งแตกต างกันที่พนื ้ ผิว เ ป น บ ริเ ว ณ แ ค บ ๆ จึง จา เ ป น ต อ ง พัฒ น า เ ค รื่อ ง ท ด ส อ บ ค ว า ม แ ข็ง ร ะ ดับ จุล ภ า ค (microhardness tester) เช น Knoop เป็ นต้ น การทดสอบแบบ Brinell • เป็ นการทดสอบความแข็งแบบนา้ าหนักคงที่ในการกดหัวกด เหล็กกล าชุบแข็งลงบนพืน้ ผิว • ชิน้ ทดสอบ โดยปกติจะใช หัวกดลูกบอลเหล็กกล าชุบแข็ง หรือทังสเตนคาร ไบด ขนาด 10 mm. • กดลงบนผิวชิน้ ทดสอบด วยนา้ หนักกด 3000 kg สาหรับโลหะ แข็ง 1500 kg สาหรับโลหะที่มีความแข็งปานกลาง และ 500 kg หรือต่า กว่ านัน้ สาหรับวัสดุอ่อนนิ่ม www.twi.co.uk/content/jk74.html การทดสอบความแข็ง Rockwell • การทดสอบ Rockwell จะทดสอบด วยนา้ หนักต างกัน สามชุดกับหัว • กดสามขนาด ส วนการทดสอบ Brinell จะมีขนาดหัวกดที่ต างไปและใช นา้ หนักกดที่มากกว ามากรวมทัง้ การทดสอบ แบบ Rockwell จะมีรอยกดที่ได มีขนาดเล็กและตืน้ กว า • ส วนวัสดุท่ นี ามาทดสอบสามารถใช กับวัสดุกล ุุ ม เดียวกันกับการทดสอบ Brinell แต สามารถทาการทดสอบ ได เร็วกว า เนื่องการทดสอบแบบ Rockwell สามารถอ านค าความแข็งได ทันทีจากหนาป ดเคร องตาม มาตรฐาน ุืุ่ ASTM E 18 • ในการทดสอบเริ่มแรกจะใช นา้ หนักกดเบือ้ งต น 10 kg ค างไว ซึ่งจะทาให เกิดรอยกดเบือ้ งต นบนชิน้ ทดสอบ โดย สังเกตเข็มบน หน าป ดเครื่องที่แสดงนา้ หนักกดเบือ้ งต นจะเข าสู • บริเวณที่กาหนดจากนัน้ ให ใส นา้ หนักกดแท จริง โดยปกติถ าใช หัวกดบอลนา้ หนักกดแท จริงจะอยู ในช วง ประมาณ 60 ถึง 100 kg และถ าใช หัวกดเพชรจะใช นา้ หนักกดแท จริงได ถึง 150 kg ส วนหัวกดบอลจะใช ขนาดเส นผ านศูนย กลาง 1/16 นิว้ และหัวกดบอลขนาด 1/8 1/4 และ 1/2 นิว้ จะใช กับวัสดุท่ อี อนกว า • หลังจากใส นา้ หนักกดแท จริงและนานา้ หนักกดออกให อ าน สเกลการทดสอบความแข็งแบบ Rockwell สเกล A B C D E F G หัวกด เพชร บอล 1/16 นิว้ เพชร เพชร บอล 1/8 นิว้ บอล 1/16 นิว้ บอล 1/16 นิว้ นา้ หนักกด (kg) 60 100 150 100 100 60 150 Principal of the Rockwell Test 1. The indenter moves down into position on the part surface 2. A minor load is applied and a zero reference position is established 3. The major load is applied for a specified time period (dwell time) beyond zero 4. The major load is released leaving the minor load applied The resulting Rockwell number represents the difference in depth from the zero reference position as a result of the application of the major load. home.iitk.ac.in/~kamalkk/ME-371.htm The Hardness Test : Rockwell Hardness Test Rockwell hardness values are expressed as a combination of a hardness number and a scale symbol representing the indenter and the minor and major loads. The hardness number is expressed by the symbol HR and the scale designation. There are 30 different scales. The majority of applications are covered by the Rockwell C and B scales for testing steel, brass, and other metals. However, the increasing use of materials other than steel and brass as well as thin materials necessitates a basic knowledge of the factors that must be considered in choosing the correct scale to ensure an accurate Rockwell test. The choice is not only between the regular hardness test and superficial hardness test, with three different major loads for each, but also between the diamond indenter and the 1/16, 1/8, 1/4 and 1/2 in. diameter steel ball indenters. If no specification exists or there is doubt about the suitability of the specified scale, an analysis should be made of the following factors that control scale selection: Type of material Specimen thickness Test location Scale limitations HR = E – e F0 = preliminary minor load in kgf F1 = additional major load in kgf F = total load in kgf e = permanent increase in depth of penetration due to major load F1 measured in units of 0.002 mm E = a constant depending on form of indenter: 100 units for diamond indenter, 130 units for steel ball indenter HR = Rockwell hardness number D = diameter of steel ball. home.iitk.ac.in/~kamalkk/ME-371.htm Advantages of the Rockwell hardness method include the direct Rockwell hardness number readout and rapid testing time. Disadvantages include many arbitrary non-related scales and possible effects from the specimen support anvil (try putting a cigarette paper under a test block and take note of the effect on the hardness reading! Vickers and Brinell methods don't suffer from this effect). www.ami.ac.uk/courses/topics/0123_mpm/index.html สเกล Rockwell อยู ในรู ปของเศษส วน 100 และแต ละค าความแข็งมี ค าความลึกรอยกดเท ากับ 0.002 mm ดังนัน้ 4 ถ าอ านค าความแข็ง ได เป น 53 HRB กับ 56 HRB หมายถึงทัง้ สองมีรอยกดต างกันเท ากับ 3 x 0.002 mm นัน้ คือ 0.006 mm สเกล B ใช ในการทดสอบวัสดุความแข็งปานกลางในช วง 0 – 100 HRB ถ าใช หัวกดบอลวัดค าความแข็งของวัสดุเกิน 100 HRB อาจทาให หัวบอลเกิดการยุบตัวทาให ได ค าความแข็งที่คลาดเคลื่อนได ส วนสเกล C มักใช ทดสอบกับวัสดุท่ ีมีค าความแข็งมากกว า 100 HRB ซึ่งปกติแล้ วเหล็กกล้ าจะมีค าความแข็งสูงสุดประมาน 70 HRC และ การวัดความแข็งด วยสเกล C จะอยู ที่ประมาณ 20 HRC ขึน้ ไป เนื่องจาก การทดสอบความแข็งต่ากว า 20 HRC ได รอยกดที่เล็กมากทาให ค าความแข็งที่ได ไม น าเชื่อถือในการทดสอบให เลือกใช สเกลที่ใช หัวกดบอลที่มีขนาดเล็กที่สุดเท าที่จะเป นไปได ทัง้ นีเ้ พราะความว องไว การทดสอบแบบ Vickers เป นการทดสอบความแข็งโดยใช หัวกดเพชรรูปป รามิดฐาน สี่เหลี่ยมจัตรุ ัสขนาดเล็ก ซึง่ มีองศาของปลายแหลม 136 องศา น ้าหนักกดที่ใช จะอยู ระหว าง 5-120 กิโลกรัม โดยจะเพิ่มครัง้ ละ 5 กิโลกรัม การทดสอบนี ้มีหลักการเดียวกันกับการทดสอบความแข็ง Brinell คือค าความแข็งที่ได คิดจากน ้าหนักกดที่กระทาต อพื ้นที่ข อง รอยกด F= Load in kgf d = Arithmetic mean of the two diagonals, d1 and d2 in mm HV = Vickers hardness www.twi.co.uk/content/jk74.html www.bestar-steel.com/cn/hardnessTesting.php http://www.nhml.com/i/resources_NHML_hardness_testing_fig2.gif Hardness of plastics and elastomers www.engineeringpolymers.com/epbb/ch09.html http://www.iun.edu/~geos/Zoran%20IUN/G%20101/Photos/Mohs%20%20scale.jpg Impact Test www.castingmanufacturers.com/facilities.asp www.wmtr.com/Content/impact_testing.htm Charpy impact test http://www.twi.co.uk/twiimages/jk71f2.gif การบ้าน : หาวิธีการคานวณหาพลังงานที่ เกิดจากการทดสอบแบบกระแทก http://www.matweb.com/reference/images/izod_apparatus.gif www.steinwall.com/ART-impact-testing.html Creep Test http://www.pktooling.co.uk/pk-images/gm-aerosol-creep-test-fixture.jpg www.twi.co.uk/content/jk81.html www.engr.usask.ca/.../geoe118/geoe118.037.html www.twi.co.uk/content/jk81.html Fatigue Test http://www.surfaceng.com/photos/large/testing_fatigue1.jpg www.risoe.dk/afm/products/mechanical/fatigue.htm www.dynaflow-inc.com/Services/matr&d.htm http://www.engrasp.com/doc/etb/mod/fm1/stresslife/Figure5.gif