Chapter 4 Nomenclatures
advertisement

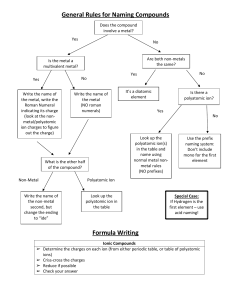
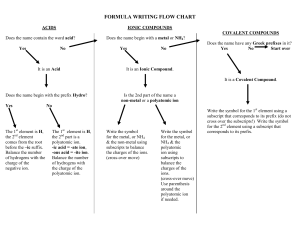
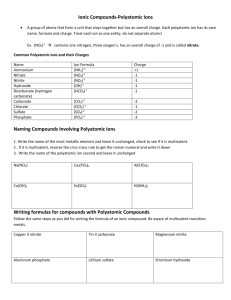
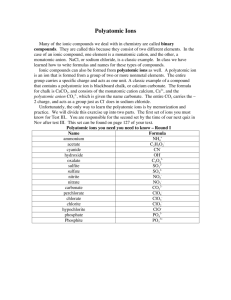
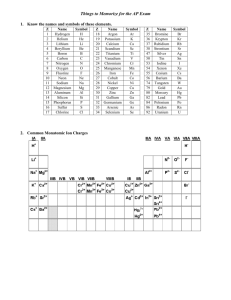
Chapter 4 Binary compounds-contain 2 elements 1) metal w/ charge and non-metal (Type I) 2) Transition metal and non-metal (Type II) 3) two non-metals (Type III) (Type I) Cation- 1st – same name as element Anion- 2nd- root + ide Examples NaI CaO 1) write element symbol and charge 2) net charges must equal zero 3) add subscripts if charges don’t add up to zero Barium sulfide Magnesium phosphide How to write formula from name 1) write element symbol and charge 2) net charges must equal zero 3) add subscripts if charges don’t add up to zero Lead (II) oxide Iron (III) sulfide Roman numeral= charge of transition metal Write name from formula • Need to figure out the charge • Include roman numeral in name FeCl2 (__x 1) + (-1 x 2)= 0 Fe+2 Iron (II) chloride ic- higher charge Fe+3 Ferric ous- lower charge Fe+2 Ferrous Example 4.2, 4.3 1) name the first element by its element name 2) second element is named as though it were an anion (ide ending) 3) prefixes are used to denote the number of atoms (Table 4.3 pg 95) 4) mono is never used for the first element Example 4.4, 4.5 Example 4.6 Polyatomic ion- charged entities composed of several atoms bound together Oxyanions- SO3 and SO4 ite ate hypo-less than per- more than ClO- hypochlorite ClO2 – chlorite ClO3 – chlorate ClO4 - perchlorate Must know - name of polyatomic ion - charge of polyatomic ion - recognize polyatomic ion NH4C2H3O2 FeSO4 Example 4.7 more than one polyatomic ion or polyatomic ions with a subscript require parentheses (NH4)2SO4 Fe3(PO4)2 Polyatomic ions names do not change Ammonium nitrate Calcium hydroxide Lead (II) sulfate Acids- when dissolved in H2O, they produce H+ ions Sour taste Naming 1) if the anion does not contain O2 then use hydro prefix, element root + ic (ex: HCl) 2) if O2 is in the anion, then look at the ending of the polyatomic ion (HNO3 and HNO2) ite- ous acid ending ate- ic Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 Iron (II) oxide FeO Example 4.9 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. HF HBr H3PO4 HNO2 Nitric acid H2SO3 H2SO4 9. Chlorous Acid 10. HClO3 11. HClO4 12. carbonic acid 13. HC2H3O2 14. HClO 15. HI 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Hydrofluoric Acid HCl Hydrobromic Acid Phosphoric Acid Nitrous Acid HNO3 Acid Sulfurous Acid Sulfuric Acid 9. HClO2 10. Chloric Acid 11. Perchloric Acid 12. H2CO3 13. Acetic Acid 14. Hypochlorous 15. Hydroiodic Acid