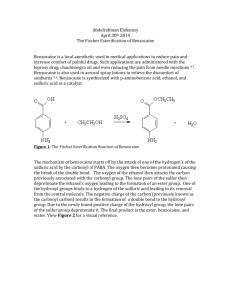
Fischer Esterification of p-aminobenzoic acid: Synthesis of
advertisement

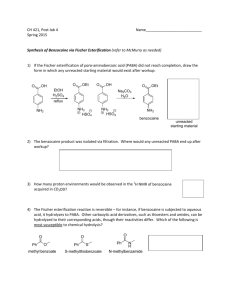
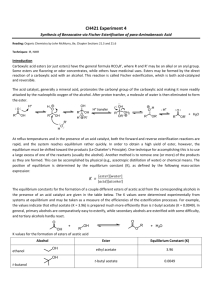
Fischer Esterification of p-aminobenzoic acid: Synthesis of Benzocaine Adapted from the Revised Procedure: Expt. 21.1 Multistep Synthesis of Benzocaine Analogs http://web.uccs.edu/bgaddis/chem338/expt21_1corr.htm To a 100-mL round bottom flask fitted with a stir bar, add 2.50 g of p-aminobenzoic acid and 20 mL of ethyl alcohol. While stirring, add 2.0 mL of concentrated H2SO4 dropwise. The precipitate that forms upon the addition of sulfuric acid should dissolve when the solution is heated. Reflux, with stirring, for 1 hour. Cool to room temperature. Neutralize cautiously with dropwise addition of 10% Na2CO3 until the pH is approximately 8. (Gas evolution will be vigorous.) Extract with two 10-mL portions of methylene chloride. Wash the combined methylene chloride layers with two 8-mL portions of water. Dry the methylene chloride solution over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Gravity filter into a clean Erlenmeyer flask containing a boiling stone. Evaporate the methylene chloride using the rotary evaporator. Recrystallize the whitish residue using as a solvent pair, ethyl alcohol and water. Suction filter the product, and let air dry. Weigh the white crystals and take the melting point. PLEASE NOTE THAT PRELAB AND POST LAB QUESTIONS ARE ON THE NEXT PAGE! Prelaboratory Questions 1. Which of the two possible amino functional groups in Procaine would be protonated first? Why? 2. What is the purpose of the sulfuric acid for this reaction? Is the acid consumed during the synthesis? Postlab Questions. 1. Write out the mechanism of your reaction. Tell what LeChatlier’s Principle is and how it applies to this procedure. What is removed to drive the reaction to completion? 2. Why did you wash with aqueous sodium bicarbonate? Explain using balanced chemical equations. 3. The oxygen from which material is incorporated into the new created ester bond? Where does the oxygen in the water originate? Benzocaine This page contains recent news articles, when available, and an overview of Benzocaine but does not offer medical advice. You should contact your physician with regard to any health issues or concerns. Overview: Benzocaine (when available) Pharmacology and use: Benzocaine is a local anesthetic commonly used as a topical pain reliever. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter analgesic ointments. It is also indicated for general use as a lubricant and topical anesthetic on intratracheal catheters and pharyngeal and nasal airways to obtund the pharyngeal and tracheal reflexes; on nasogastric and endoscopic tubes; urinary catheters; laryngoscopes; proctoscopes; sigmoidoscopes and vaginal specula. For general use as a lubricant and topical anesthetic on esophagus, larynx, mouth, nasal cavity, rectum, respiratory tract or trachea, urinary tract, vagina. It is also used to suppress gag reflex. Mechanism Of Action: Benzocaine binds to sodium channel and reversibly stabilizes the neuronal membrane which decreases its permeability to sodium ions. Depolarization of the neuronal membrane is inhibited thereby blocking the initiation and conduction of nerve impulses. Doctors unsure what causes canker sores - 20 Apr 2009 Liquids or ointments with a numbing ingredient, such as benzocaine (Anbesol, Oragel, Orabase, Zilactin-B, Tanac) help relieve the discomfort of canker News-Leader.com Family Doctor: Chiggers can spoil a day of outdoor fun - Apr 9, 2009 Its active ingredients are precipitated sulfur and benzocaine, which work together for quick relief. It can also be used for mosquitoes, fleas, no-see-ums, Canton Repository Collingham OAP stashed cocaine in washing machine - Mar 31, 2009 Police also found a 1kg bag of cocaine cutting agent Benzocaine in the tumble dryer at 65-yearold Michael Hunter's home in Collingham near Wetherby. Yorkshire Evening Post http://www.mongabay.com/health/medications/Benzocaine.html