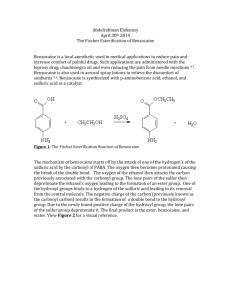
Microsoft Word
advertisement

Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving LINDANE (Kwell) ASSESSMENT POTENTIAL NURSING DIAGNOSES Prior to administration: ■ Obtain complete ■ health history including allergies, drug history, and possible drug Deficient Knowledge, related to no previous contact with lice or mites or treatment ■ interactions. Treatment Regimen Noncompliance, related to knowledge deficit, embarrassment ■ Assess vital signs. ■ Assess skin for presence of lice and/or mite ■ Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity, related to lesions and itching infestation, skin lesions, raw or inflamed skin, and open cuts. ■ Obtain history of seizure disorders. ■ Obtain patient’s age. ■ Assess pregnancy and lactation status. ■ Obtain social history of close contacts, including household members and sexual partners. PLANNING: PATIENT GOALS AND EXPECTED OUTCOMES ■ Patient and significant others will be free of lice or mites and experience no reinfestation. ■ Patient will express an understanding of how lice and mites are spread, proper administration of lindane, necessary household hygiene, and the need to notify household members, sexual partners, other close contacts such as classmates of infestation. ■ Skin will be intact and free of secondary infection and/or irritation. IMPLEMENTATION Interventions and (Rationales) ■ Patient Teaching/Discharge Planning Monitor for presence of lice or mites. Instruct patient and caregiver to: (This determines the effectiveness of drug ■ therapy.) Examine for nits on hair shafts; lice on skin or clothes; inner thigh areas; seams of clothes that come in contact with axilla, neckline, or beltline ■ Examine for mites between the fingers, on the extremities, axillary and gluteal folds, around the trunk, and in the pubic area ■ Apply lindane properly. (Proper application is Instruct patient and caregiver: critical to elimination of infestation.) ■ To wear gloves during application, especially if applying lindane to more than one person, or if pregnant ■ That all skin lotions, creams, and oil-based hair products should be removed completely by scrubbing the whole body well with soap and water, and drying the skin prior to application ■ To apply lindane to clean and dry affected body area as directed, using no more than 2 oz per application ■ That eyelashes can be treated with the application of petroleum jelly twice a day for 8 days followed by combing to remove nits ■ To use fine-tooth comb to comb affected hair following lindane application to the hair and scalp to treat all household members and sexual contacts simultaneously ■ To recheck affected hair or skin daily for 1 week after treatment ■ Inform patient and caregivers about proper care Instruct patient and caregiver to: of clothing and equipment. (Contaminated ■ articles can cause reinfestation.) Wash all bedding and clothing in hot water, and to dry-clean all nonwashable items which came in close contact with patient ■ Clean combs and brushes with lindane shampoo and rinse thoroughly EVALUATION OF OUTCOME CRITERIA Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving BENZOCAINE (Solarcaine) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration: Comfort, impaired, related to presence Obtain complete health history including of sunburn, burns, toothache, ear allergies, drug history and possible drug infections, etc. interactions. Knowledge, deficient, related to lack of Assess for presence/history of sunburn, proper education regarding health minor burns, serious burns, mild pruritus practices necessary to prevent sunburn, burns, etc. and lack of previous contact with benzocaine Noncompliance, overuserelated to reluctance to contact health care provider if symptoms continue past recommended maximum usage time Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes Patient will: Experience improvement in symptoms without complications Demonstrate proper use of benzocaine Demonstrate necessity to contact health care provider if symptoms do not improve, or worsen, by the time maximum recommended usage is reached Demonstrate knowledge of measures to take to prevent sunburn, burns, etc. from occurring in future Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Teach patient to: Monitor for secondary infection. (Drug should not be used if infection is present Examine affected areas prior to each in area of sunburn or insect bites.) application of benzocaine Discontinue use of benzocaine if redness, swelling, pain appears or worsens Monitor status of burns. (Drug should not Advise patient that : be used if serious burns are present.) Benzocaine cannot be used on burns deeper than one skin layer or if skin is broken and/or weeping If pain is not present, it can be an indicator of the seriousness of burn, since nerve endings may have been damaged Advise patient and caregiver: Monitor for perforated tympanic membrane or discharge from ear(s). to use caution whenever applying to the external ear to prevent its getting into the inner ear not to use without health care provider approval if patient has pain in ear, decreased hearing, discharge Monitor for proper use. (Since Instruct patient: benzocaine is OTC medication, patient To use only on intact skin, to avoid eyes, may not understand proper use or areas of local sepsis precautions.) That benzocaine is to be used no more than 7 days To discontinue benzocaine if symptoms of hypersensitivity occur (redness, pain, rash, heat) and to contact health care provider if pain lasts longer than 48 hours To do not chew gum or eat until anesthetic effects of benzocaine used for toothache relief have worn off In infant proper use of benzocaine for relief of teething Instruct patient to discontinue use of Monitor for worsening of condition. benzocaine and contact health care provider if increased pain, pruritus, heat, or other symptoms occur. Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving ISOTRETINOIN (Accutane) ASSESSMENT POTENTIAL NURSING DIAGNOSES Prior to administration: ■ ■ Disturbed Body Image, related to presence of Obtain complete health history including acne and possible worsening of symptoms after allergies, drug history, and possible drug treatment begins interactions. ■ Decisional Conflict, related to desire for ■ Obtain pregnancy and lactation status. pregnancy, and necessity of preventing ■ Assess for history of psychiatric disorders. pregnancy during therapy with isotretinoin ■ Assess vital signs to obtain baseline information. ■ Noncompliance, related to length of treatment time, failure to use effective contraception ■ Impaired Skin Integrity, related to inflammation, redness, scaling, secondary to treatment PLANNING: PATIENT GOALS AND EXPECTED OUTCOMES The patient will: ■ Experience decreased acne, without side effects or adverse reactions ■ Demonstrate acceptance of body image ■ Demonstrate an understanding of the drug’s action by accurately describing drug side effects and precautions IMPLEMENTATION Interventions and (Rationales) ■ Monitor lab studies during treatment, including Patient Education/Discharge Planning ■ blood glucose. Instruct patient on importance of lab studies prior to therapy and periodically during therapy and doing home blood glucose monitoring if diabetic. ■ Discuss potential adverse reactions to drug Instruct patient to therapy. (Understanding of drug effects is ■ important for compliance.) Use two forms of reliable birth control for 1 month before beginning treatment, during treatment, and for 1 month following completion of treatment ■ Not donate blood during treatment and for a minimum of 4 weeks after completion of treatment; isotretinoin in donated blood could cause fetal damage if given to a pregnant woman ■ Talk with pediatrician about alternative methods of feeding if breastfeeding ■ Monitor for cardiovascular problems. (Use ■ Avoid use of vitamin A products ■ Discuss with patient importance of complete isotretinoin with caution in patients with heart disclosure regarding medical history and block, especially if patient is also taking a beta- medications. blocker.) ■ Monitor emotional health. (Patient may become Instruct patient: depressed secondary to acne itself, length of ■ treatment, possibility of worsening symptoms at beginning of treatment, changed body image, or Regarding signs and symptoms of depression and to report ■ drug itself.) To report signs of depression or any feelings of suicide ideation immediately and discontinue isotretinoin ■ ■ Monitor CBC, blood lipid levels, glucose levels, ■ Teach patient importance of a complete workup liver function tests, eye exam, GI status, prior to starting isotretinoin therapy and urinalysis. periodically during course of treatment. Monitor for vision changes. (Corneal opacities Instruct patient: and/or cataracts may develop as result of ■ isotretinoin use. Dryness of eyes during To report any decreased vision and discontinue use of isotretinoin treatment is common. Night vision may be ■ To avoid driving at night if possible diminished during treatment.) ■ Use of artificial tears to relieve dry eyes ■ That use of contact lenses may need to be discontinued during therapy ■ Monitor alcohol use. (Alcohol use with Advise patient to: isotretinoin leads to increased triglyceride ■ levels.) Eliminate or greatly reduce alcohol use, including alcohol-containing preparations such as mouthwashes or OTC medications ■ ■ Read labels for alcohol content Monitor skin problems. (This will determine the Advise patient: effectiveness of drug therapy.) ■ That acne may worsen during beginning of treatment ■ To monitor skin for improvement in 4 to 8 weeks; if no improvement is noted, patient should contact primary healthcare provider ■ Monitor for side effects: headache (especially if accompanied by nausea and vomiting), fatigue, ■ Instruct patient regarding possible side effects and to report immediately if any occur depression, lethargy, severe diarrhea, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, dry mouth, hematuria, proteinuria, liver dysfunction (jaundice, pruritus, dark urine. Report immediately EVALUATION OF OUTCOME CRITERIA Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”).