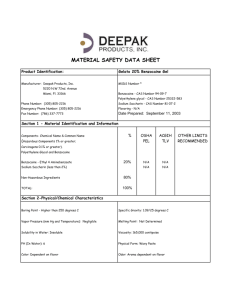
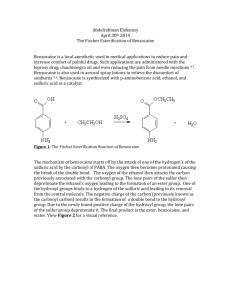
Benzocaine synthesis
advertisement

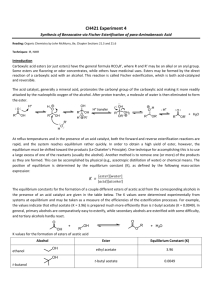
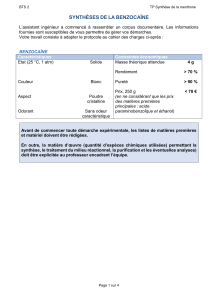
CH 421, Post‐lab 4 Name___________________________ Spring 2015 Synthesis of Benzocaine via Fischer Esterification (refer to McMurry as needed) 1) If the Fischer esterification of para‐aminobenzoic acid (PABA) did not reach completion, draw the form in which any unreacted starting material would exist after workup: O O OH OEt O OH EtOH H2SO4 O OEt Na2CO3 H2O reflux NH2 NH3 HSO4 NH3 HSO4 NH2 benzocaine unreacted starting material 2) The benzocaine product was isolated via filtration. Where would any unreacted PABA end up after workup? 3) How many proton environments would be observed in the 1H NMR of benzocaine acquired in CD3OD? 4) The Fischer esterification reaction is reversible – for instance, if benzocaine is subjected to aqueous acid, it hydrolyzes to PABA. Other carboxylic acid derivatives, such as thioesters and amides, can be hydrolyzed to their corresponding acids, though their reactivities differ. Which of the following is most susceptible to chemical hydrolysis? 5) Many esters can be hydrolyzed with aqueous NaOH, though reactivities depend heavily on sterics. The first step in the mechanism of ester hydrolysis under basic conditions is a nucleophilic attack of hydroxide on the carbonyl carbon. Considering this, which of the following esters is expected to be most readily hydrolyzed with aqueous base: a. ethyl butanoate b. propyl butanoate c. isopropyl butanoate d. tert‐butyl butanoate 6) Draw the structures of the following carbonyl compounds: N,N‐diethylpropionamide isobutyryl chloride allyl hexanoate 7) Delocalization of a carbonyl pi bond shifts the C=O infrared absorption to a lower frequency (corresponding to a lower wavenumber, cm‐1). Which of the following carboxylic acid derivatives would have the highest wave number (cm‐1) in the IR spectrum? a. Acetic anhydride b. Ethyl acetate c. N,N‐dimethylformamide d. Benzoic acid 8) Look up the mechanism for acid‐catalyzed acetal/ketal formation from aldehydes/ketones. Which of the following is not an intermediate in the mechanism for formation of acetone dimethyl ketal from acetone and methanol? O cat. acid + O Me H A MeO 2 MeOH OMe O O O Me H B OMe + H2O H OH H O H OMe O Me C D Me E 9) Complete the following schemes. O O excess NaOH H2O / EtOH O 10) ‐Hydrogens are acidic, and this property can be utilized in target syntheses (e.g. aldol reaction, alkylation reaction, etc.) While this property can be useful, some substrates may undergo an undesired racemization under acidic or basic conditions via enolate or enol formation, respectively. Indicate “yes” or “no” whether the following compounds are prone to racemization under these conditions. O O NH Ph CHO Ph Ph OAc