Lab #7
advertisement

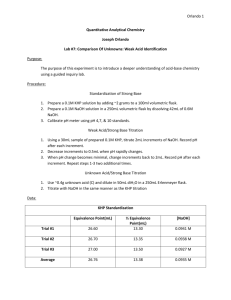
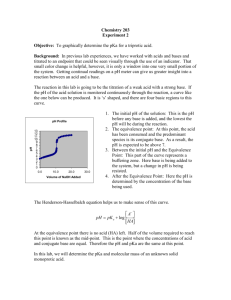
Experiment 7: Comparison of Unknowns: Weak Acid Identification October 24, 2011 Objective: The purpose of this experiment is to become more familiar with acid-base chemistry. The necessary equations will need to be derived for this experiment and the groups with the same unknown need to be identified. Procedure Part 1: 1) Obtain a weak acid unknown 2) Titrate the acid with a strong base 3) Calculate the correct amount of KHP to use Part 2: 1) Fill weighing bottle halfway with KHP from oven and place it in dessicator to cool 2) Weigh approximate amount of calculated KHP and place in a 250mL Erlenmeyer (3 samples) 3) Standardize pH meter 4) Dissolve KHP in 50mL of water and add base in 2-3mL additions, checking pH 5) Graph mL of base added vs. pH and identify equivalence point and half equivalence point Part 3: 1) How many mL of base were used, which is determined by the equivalence point, is equal to the number of moles present 2) Calculate the pH before any base is added, at the equivalence point, and at the half equivalence point Part 4: 1) Take into account the fact that a strong acid is one that is 100% ionized and calculate the pH and concentrations Part 5: 1) Find the acid dissociation constant 2) Predict the shape of the curve when dealing with a weak acid, titrated by a strong base Part 6: 1) Titrate the weak acid 2) Find the 2 points on this titration that will help identify the unkown Part 7: 1) Calculate the MW and Ka of the unknown acid Data Grams of KHP (g) Equivalence point (mL) Half equivalence point (mL) Trial 1 0.6131 Trial 2 0.6120 Trial 3 0.6135 28.50 25.5 26.5 14.25 12.75 13.25 Average 0.6130 26.8 13.41 Trial #1 mL added 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 28 28.5 29 29.5 30 32 34 37 pH 4.02 4.33 4.57 4.77 4.95 5.12 5.30 5.52 5.82 6.32 6.90 9.20 10.69 11.03 11.17 11.55 11.73 11.89 Trial #2 mL added 0 5 10 15 20 25 27 28 29 29.5 30 31 33 36 39 pH 4.07 4.48 4.84 5.11 5.42 5.85 6.18 6.46 8.31 10.68 11.0 11.28 11.59 11.81 11.94 Trial #3 mL added 0 4 8 11 14 17 20 23 26 27 27.5 28 28.5 29 29.5 30 32 34 37 pH 4.01 4.40 4.70 4.88 5.05 5.23 5.41 5.65 6.04 6.21 6.36 6.58 6.95 9.61 10.65 11.02 11.48 11.69 11.88 Unknown Weak Acid: Grams of KHP (g) Equivalence point (mL) Half equivalence point (mL) Trial #1 mL added 0 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 pH 2.94 3.31 3.89 4.11 4.35 4.68 5.39 10.81 11.23 11.41 11.56 11.67 Trial 1 0.1008 Trial 2 0.10158 Trial 3 0.1060 8.0 9.0 7.5 4.0 4.5 3.75 Trial#2 Trial#3 mL mL added pH added pH 0 3.01 0 3.00 1 3.40 1 3.39 2 3.69 2 3.69 3 3.94 3 3.93 4 4.18 4 4.14 5 4.43 5 4.38 6 4.74 6 4.70 6.5 4.93 6.5 4.92 7 5.38 7 5.25 7.5 10.20 7.1 5.30 8 11.03 7.2 5.41 9 11.43 7.3 5.54 10 11.61 7.4 5.75 11 11.75 7.5 6.28 12 11.84 7.6 9.42 7.8 10.13 8 11.33 9 11.54 10 11.69 11 11.79 Average 0.1028 8.17 4.08 pH Trial #1 Trial#2 Trial#3 Average Std. Dev Before Based added 3.750 3.625 3.775 3.717 0.003215 At equivalenc e point 7.5 7.25 7.55 7.43 0.003215 1mL after equivalence point 11.11 11.13 11.10 11.11 0.000577 *pKa – pH at half-euivalence point Calculations Grams of KHP to produce 25 mLs of Titrant 0.1M = moles base = .003mol .030L moles of acid=moles of base .003mol KHP x 204.2212g = .6127g Molarity of NaOH (Moles of acid=Moles of Base) – mol KHP = .003mol Molar Mass (g/mol) 134.4 140.0 140.4 138.3 0.69048 pKa 4 4.06 4.04 4.03 0 Ka 1x10-4 8.71x10-5 9.12x10-5 8.92x10-5 0 .003 moles NaOH = .105M NaOH .0285 L NaOH pH: (Using Trial 1 for example calculations) Before Base added: 1 mol KHP x .6131g KHP = .003mol KHP = mol HP204.2212g .003 mol HP- = 0.060M HP.05L I C E 0.0500 -x 0.0500-x +x +x +x +x 3.96 x 10-6 = x2 0.0500-x x=4.45 x 10-4 -log(4.45 x 10-4) = 3.35 At equivalence point: 1 mol KHP x .6131g = .003mol KHP = mol HP204.2212g .003 mol KHP = .0382M P2.0785L I C E 0.0382 -x 0.0382-x +x +x +x +x Kw= 1 x 10-14 Kb = 2.56 x 10 2.56 x 10-9 = -9 x2 .03382-x x=9x10-6 -log(9x10-6) = 5.04 = pOH 14-5.04 = 8.96 = pH 1 mL after equivalence point: 1 mol KHP x .6131g KHP = .003mol KHP = mol HP204.2212g .003mol HP- = .0377M P2.0795L I C E 0.0377 -x 0.0377-x Kb = 2.53x10-9 +x +x +x +x 2.53x10-9 = x2 .0377-x x= 9.81x10-6 = -log(9.81x10-6) = 5.01 14-5.01 = 8.99 = pH An ice table is required for a weak acid because the formal concentration taken into consideration is not completely dissociated. The Ka is used to determine how much is dissociated. Strong acids completely dissociate. A small jump is predicted in the curve for a weak acid titrated by a strong base Molar Mass of Unknown: 7.5L x 0.1M NaOH = .75mol NaOH .1008g = 134.4g unk .75mol Ka of unknown: At half-equivalence point, pH = pKa = 4 Ka = 1x10-4 Conclusion The unknown acid was found to be benzoic acid. This was based on the molecular weight, pKa, and Ka values. The molecular weight was a little off at 122g as well as the Ka value of 6.28x10-5. The pKa value, however, was relatively close at 4.202.