Weak Acid Identification Lab Report: Quantitative Analysis
advertisement

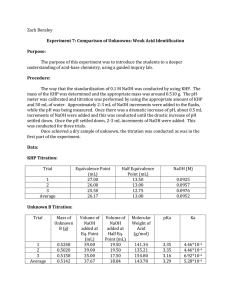
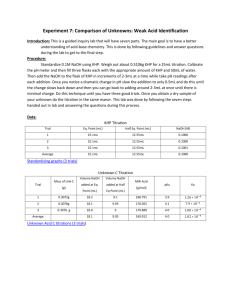
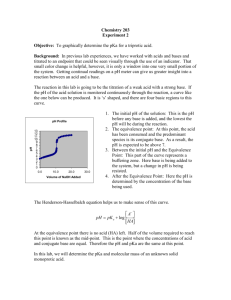
Orlando 1 Quantitative Analytical Chemistry Joseph Orlando Lab #7: Comparison Of Unknowns: Weak Acid Identification Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to introduce a deeper understanding of acid-base chemistry using a guided inquiry lab. Procedure: Standardization of Strong Base 1. Prepare a 0.1M KHP solution by adding ~2 grams to a 100ml volumetric flask. 2. Prepare a 0.1M NaOH solution in a 250mL volumetric flask by dissolving 42mL of 0.6M NaOH. 3. Calibrate pH meter using pH 4,7, & 10 standards. Weak Acid/Strong Base Titration 1. Using a 30mL sample of prepared 0.1M KHP, titrate 2mL increments of NaOH. Record pH after each increment. 2. Decrease increments to 0.5mL when pH rapidly changes. 3. When pH change becomes minimal, change increments back to 2mL. Record pH after each increment. Repeat steps 1-3 two additional times. Unknown Acid/Strong Base Titration 1. Use ~0.4g unknown acid (C) and dilute in 50mL diH2O in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask. 2. Titrate with NaOH in the same manner as the KHP titration Data: KHP Standardization Equivalence Point(mL) Trial #1 26.60 ½ Equivalence Point(mL) 13.30 [NaOH] Trial #2 26.70 13.35 0.0938 M Trial #3 27.00 13.50 0.0927 M Average 26.76 13.38 0.0935 M 0.0941 M Orlando 2 Unknown Titration Mass(g) Acid used Equivalence Point(mL) 23.00 ½ Equivalence Point(mL) 11.50 Molecular Weight of Acid(g/mol) 136.56 Trial #1 0.3008 Trial #2 pKa 4.10 0.3068 24.00 12.00 132.54 4.10 Trial #3 0.3102 26.50 13.25 133.15 4.10 Average 0.3059 24.50 12.25 133.46 4.10 Ka 7.94 × 10−5 Equations: [NaOH] 2.0464𝑔 𝐾𝐻𝑃 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐻𝑃 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 1 30𝑚𝐿 × × 𝑥 = 0.09356 𝑀 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 204.23 𝑔 𝐾𝐻𝑃 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐾𝐻𝑃 0.02676 𝐿 𝑡𝑖𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑡 100𝑚𝐿 Molar Mass (g/mol) of Unknown Acid . 0245 𝐿 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 × 0.09356 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑈𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 × = 0.002292 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑈𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 1𝐿 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 0.3059 𝑔 𝑈𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 𝑢𝑠𝑒𝑑 = 133.46 𝑔/𝑚𝑜𝑙 0.002292 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑈𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 Ka 𝐾𝑎 = 10−𝑝𝐾𝑎 = 10−4.1 = 7.94 × 10−5 Possible Identity of Unknown Acid Ka pKa Benzoic Acid Molecular Weight(g/mol) 122.12 6.28E-5 4.202 2,4-Dinitrophenol 184.106 7.69E-5 4.114 3-Chloropropanoic Acid 105.52 7.8E-5 4.108 2,2-Bipyridine 156.15 4.6E-5 4.337 Orlando 3 KHP Standardization 14.00 13.00 12.00 11.00 10.00 9.00 pH 8.00 7.00 6.00 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 1.00 0.00 0.00 5.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 25.00 mL NaOH Titrated 30.00 35.00 40.00 Unknown Weak Acid-Strong Base Titration 13.00 12.00 11.00 10.00 9.00 pH 8.00 7.00 6.00 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 1.00 0.00 0.00 5.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 mL NaOH added 25.00 30.00 35.00 40.00 Orlando 4 Conclusion: The purpose of this experiment was to determine the identity of an unknown acid. The unknown acid that we used was unknown acid C. Upon completion of the titrations, we were able to determine the equivalence point and half equivalence point of Unknown C by viewing the titration curves. Using the information gathered from the titrations, we were able to determine the Ka, pKa, and molecular weight of Unknown Acid C. Since the Ka (7.94E-5) and the molecular weight (133.46 g/mol) were known, the possible identity of our unknown could be narrowed down to several acids including benzoic acid (Ka=6.28E-5, MW=122.12) and 2,4Dinitrophenol (Ka=7.69E-5, MW=184.106 g/mol). However, since only benzoic acid's MW was similar to our unknown's MW, it was concluded that Unknown C was in fact Benzoic Acid. Although our data did not exactly match the data given for Benzoic Acid due to possible random and systematic error, our experiment proved successful in determining the identity of our unknown.