P 2
advertisement

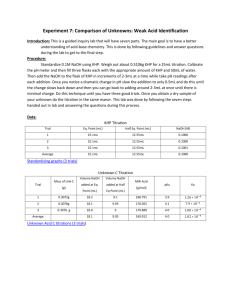
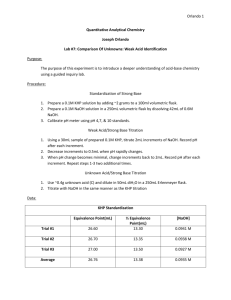
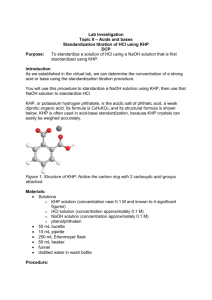
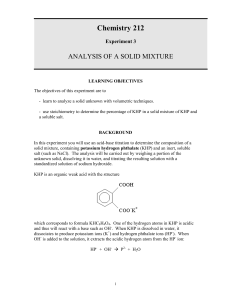
Volumetric Acid Determination Week 1 - Standardize NaOH w/ pure KHP Determine Unknown %KHP Week 2 – Continue Unknown % KHP pH meter titration of an unknown acid From last week…why Boil Water for Preparation of NaOH Solution? CO2(g) + H2O() H2CO3(aq) H2CO3(aq) + H (aq) - + HCO3 (aq) Ka = 4.3 x 10 Protons from carbonic acid can neutralize hydroxide ions thus changing the concentration of OH- in the solution. Also forms Na2CO3, slightly insoluable salt. -7 KHP is potassium hydrogen phthalate KHP K+(aq) + HP–(aq) Ka = 3.91 x 10-6 MW = 204.2236 HP–(aq) + OH– (aq) → P2– (aq) + H2O() Selection of Indicator pH? Kb = [HP-][OH-] ─────── = 2.56 x 10-9 [P2-] P2- + H2O [P2-]-x → HP- + OHx x at equilibrium [P2-] = n(P2-)/Vol n(P2-) = 0.5 g/204.2236 g/mol = .00245 mol V(OH-) = .00245 mol/(.08 mol/L) = 30 mL = .030 L approximately Vtotal = 50 + 30 mL = 0.080 L [P2-] = 0.00245 mol/ (.080 L) = .030 M x2 HP- + OH- → P2- + H2O complete at endpoint ───── = 2.56 x 10-9 ; x = 8.76 x 10-6 = [OH-] .030 – x P2- + H2O → HP- + OH- K = ? = Kb = Kw/Ka Let’s derive it … pOH = 5.063 ; pH = 14 - 5.063 = 8.937 + 2H + P → HP 1/Ka H2O → H+ + OHKw ________________________ P2- + H2O → HP- + OH- Kb = Kw/Ka = (1.00 x 10-14)/(3.91 x 10-6) = 2.56 x 10-9 Phenolphthalein -O OH O OH O + 2OH - O- + 2 H2O O O H2In (colorless) In-2 (pink) The color change in phenolphthalein is due to a change in structure of the molecule. In acid, the molecule is in its H2In form containing a central 5-membered ring, which is somewhat strained. In base the In-2 structure opens up and becomes flatter. Procedure • • • • Dissolve KHP in ~50 mL DI water, warm if necessary Add 2-3 drops of indicator Titrate until faint pink persists For the unknown %KHP, adjust mass appropriately for ~35mL Calculations Quick Check of Precision Use vol(base) mass(acid ) to calculate high low 1000 2 ppt average To determine % KHP vol NaOH moles NaOH moles KHP mass KHP mass% KHP (concentration of NaOH) (stoichiometry) (molar mass) mass KHP x 100% mass sample Week 2 Start unknown %KHP Then go back to pure KHP if necessary pH meter- half the class starts first, then teach the second half by 3:15 PM Continue titrations with time left Clean up after yourselves Strong Base/Weak Acid Titration Curve OH-, A- pH AInflection Point HA & A- Equivalence Point HA only Volume of NaOH Use the equivalence pt & halfway equivalence point for calculations...how? End point needs to be past the equivalence point Determination of Ka • Use pH meter data to create titration curve • Dissolve 0.4 g of acid (not KHP, record to .1mg) in 250 mL beaker with ~75 mL of water • Record pH every .2-.3 unit change or every 5mL • Graph paper from me (better than printer) Then clean up after yourselves! Wash vials and leave on rack near storage dessicators and ovens. Otherwise, points will be deducted!!!