HCl Standardization Titration Lab with KHP
advertisement

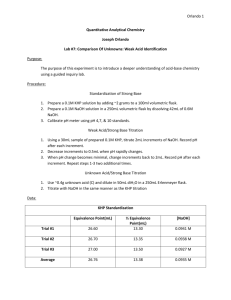
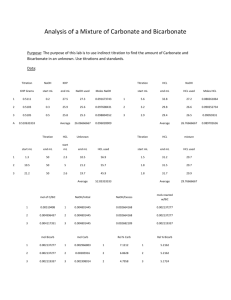
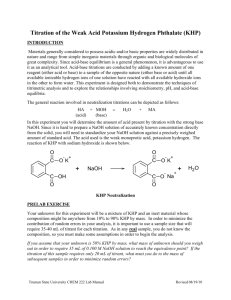
Purpose: Lab Investigation Topic 8 – Acids and bases Standardization titration of HCl using KHP DCP To standardize a solution of HCl using a NaOH solution that is first standardized using KHP. Introduction As we established in the virtual lab, we can determine the concentration of a strong acid or base using the standardization titration procedure. You will use this procedure to standardize a NaOH solution using KHP, then use that NaOH solution to standardize HCl. KHP, or potassium hydrogen phthalate, is the acidic salt of phthalic acid, a weak diprotic organic acid. Its formula is C8H5KO4, and its structural formula is shown below. KHP is often used in acid-base standardization, because KHP crystals can easily be weighed accurately. Figure 1: Structure of KHP. Notice the carbon ring with 2 carboxylic acid groups attached. Materials: Solutions o KHP solution (concentration near 0.1 M and known to 4 significant figures) o HCl solution (concentration approximately 0.1 M) o NaOH solution (concentration approximately 0.1 M) o phenolphthalein 50 mL burette 10 mL pipette 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask 50 mL beaker funnel distilled water in wash bottle Procedure: 0. 1. Rinse all glassware with distilled water. Rinse beaker with KHP solution. Rinse burette with NaOH solution. The Erlenmeyer flask should not be rinsed with either solution. 2. Pipette 10 mL of KHP solution into the Erlenmeyer flask. Add a few drops of phenolphthalein. Fill the burette with NaOH solution. 3. Titrate the KHP solution with the NaOH solution. You should try to get a very pale pink endpoint. Repeat your titration until you get 3 consistent titration volumes (within 0.1 mL). 4. Repeat Steps 1 to 3 using HCl instead of KHP. Data Processing and Analysis: 0. 1. Using your data from the KHP/NaOH titrations, determine the concentration of the NaOH solution and the uncertainty of that concentration. 2. Using this value and your data from the HCl/NaOH titrations, determine the concentration of the HCl solution and the uncertainty in that concentration.