Aldehydes and Ketones

CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
- Aldehydes and Ketones
• Structure
• carbonyl groups consists of a carbon-oxygen double bond
• the bond is polar due to the difference in electronegativity
aldehydes and ketones differ in what is attached to the carbon.
• ALDEHYDES - at least one H attached
• KETONES - two carbons attached
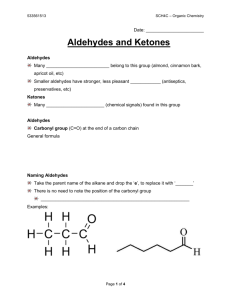
Aldehydes
• Functional group: CHO, and is always at the end.
• Replace the “e” of the alkane with “ al ”
• Isomers of C
3
H
7
CHO (x2)
• C=O strongly polar
• No hydrogen bonding, high boiling point
• • substituent's are numbered based on the C with the O being number 1
Preparation of ethanal
• Chemicals: ethanol and sodium dichromate
• Word equation: ethanol + sodium dichromate
= ethanal + water
• Chemical equation:
• Sodium dichromate is an oxidising agent.
• Cr(+6) + 3e = Cr(+3)
• Orange green
• Alcohol is in excess to prevent further oxidation to the acid.
• Ice around the collecting flask to cool the ethanal as it has a low boiling point.
• Set up is for distillation.
Reactions of ethanal
• Fehlings 1 and 2: royal blue to red brick precipitate.
• Cu
2
O formed
• Cu(+2) + e = Cu(+1)
• Blue red
• Ammoniacal silver nitrate(Tollen’s reagent)
• Warmed
• Ethanal oxidised to ethanoic acid
• Ag(+) + e = Ag
• Aldehydes reduced the silver/ ketones don’t
• Acidified potassium permanganate:
• Purple to colourless
• Mn(+7) oxidised to Mn(+2)
ketones
• The carbon with the C = O must be attached to two other carbons.
remove E from the equivalent alkane name and add ONE
• if necessary, the position of the C=O is given
(lower number counting from one end)
• Draw up to 4 carbons and name