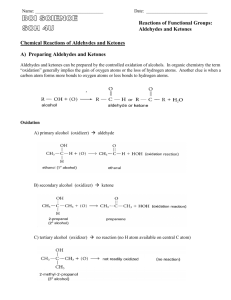
aldehyde ketone
advertisement

13.7 Aldehydes and Ketones Structures. Two series of organic compounds containing C=O carbonyl group. Aldehydes have a hydrogen attached to the carbonyl group. Two groups react differently and can be distinguished. aldehyde ketone Aldehydes Now try these:- Named using suffix - al. E.g. HCHO methanal CH3CHO ethanal propanal pentanal Ketones Name use suffix -one. E.g. CH3COCH3 propanone Ketones with 5 or more carbons have structural isomers eg. CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3 & CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3 Draw the structures and name these isomers. Now try these: CH3CH2CH2CH2COCH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2COCH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3COCH2CH3 CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH2CH3 Preparation of aldehydes and ketones Oxidation of alcohols Acidified potassium dichromate - heat under reflux. Orange dichromate Cr2O72- is reduced to green Cr3+ in solution. Primary alcohol aldehyde carboxylic acid Secondary alcohol ketone. Redox reactions Oxidation of alcohols are redox reactions. Oxidation of ethanol; CH3-CH2-OH CH3-CHO + 2H+ + 2e CH3-CHO + H2O CH3COOH + 2H+ + 2e reduction; Cr2O72-(aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6e- 2Cr3+ (aq) +7H2O orange green Reactions - oxidation Aldehydes have a hydrogen atom next to the carbonyl group - easily oxidised. Fehlings solution - Cu2+(aq) ions (in alkali) reduced to Cu+ - blue to brick red. Aldehyde oxidised to carboxylic acid. Ketones not oxidised easily by either Fehlings solution or acidified dichromate. Reactions - reduction Powerful reducing agent needed. NaBH4 - sodium tetrahydridoborate (III) Aldehydes reduced to primary alcohols. Ketones reduced to secondary alcohols. Reactions - addition Carbonyl groups can undergo addition reactions. HCN in presence of alkali. Adds across C=O to form 2 hydroxynitriles (cyanohydrins) Nucleophilic addition