Molecular Geometry and Polarization
advertisement

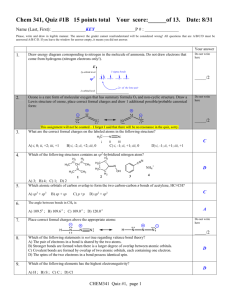
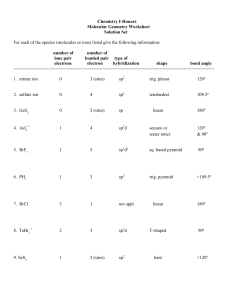
2/27/2012 Molecular Geometry and Polarization Shapes of Molecules Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) a. Bonded electrons b. Lone Pairs 1. Linear (180o) BeH2 CO2 2. Trigonal Planar (120o) NO3- 3. Tetrahedral (109.5o) CH4 1 2/27/2012 4. Trigonal Pyramidal (~107o) NH3 5. Bent (~104.5o) H2 O H O H SO2 2 2/27/2012 6. Trigonal Bipyramid (120o, 90o) PCl5 7. Octahedral (90o) SF6 Shapes of Molecules Ex: Multiple Bonds: N2 H2CO HCN SO2 Shapes of Molecules Models Activity 3 2/27/2012 SO22+ SO22SO2 SO3 SF3PF4XeCl5+ BrF4- Predict the molecular geometry of: WarmUp SnCl3O3 SeCl2 CO32SF4 IF5 ClF3 ICl4- ClF4SiCl3SO2 SCl4 SeO3 BrCl5 BrCl3 4 2/27/2012 Polar Molecules 1. Polar molecule – Overall, the electrons are attracted more to one end of an entire molecule 2. Non-Polar Molecule – The electrons are spread out evenly over the entire molecule -/ + Partial (not full) charges Electron Density Examples: H2 CH4 H2 H 2O CH4 H2CO H 2O H2CO 5 2/27/2012 Polar Molecules BeCl2 NH3 CO2 SO2 SF6 BCl3 CH2Cl2 Hybrid Orbitals • A mixing of the atomic orbitals (s, p, d, f) of the central atom • Electrons no longer move in the old orbitals, but in a new pattern BeF2 Isolated Be 1s22s2 (Note that all Be: electrons are paired) To bond Be must unpair some electrons: Bonded Be 1s22s12p1 •Be• 6 2/27/2012 • Be is called an “sp” hybrid. • Drawings: Isolated Be BeF2 CH4 Isolated C 1s22s22p2 Bonded C 1s22s12p3 Isolated C Effect of Lone Pairs • Lone pairs do count towards hybridization • Ex: H2O Bonded C sp3 7 2/27/2012 Try BF3 Examples CCl4 NH3 PF5 SF6 XeF4 BrF3 PH3 H2S SF5SF4 CO32HCN BrCl3 CH4 Hybrid Orbitals and Multiple Bonds • sigma ( ) bonds – single bonds formed by hybrid orbitals • pi ( ) bonds – double or triple bonds, not formed by hybrid orbitals H H–H C=C H One bond H :N=N: H One bond plus one bond One bond plus two bonds 8 2/27/2012 • Consider C2H4 • Each C is sp2 • Double bond does not count toward hybridization • Consider C2H2 • Each C is sp hybridized • Two bonds do not count toward hybridization What is the hybridization and bonding types for H2CO? Also, what are the bond angles? Delocalized Bonding What is the hybridization and bonding types for acetonitrile (shown)? Also, what are the bond angles? • Adjacent multiple bonds can overlap. • Benzene (C6H6) • All bond lengths are equal H H - C -C=N: H 9 2/27/2012 Use hybrid orbital theory to explain why all the bonds in the NO3- ion are of equal length 10 2/27/2012 12 a) ~110o b) BF3 flat (no lone pair) 21. a) (lin)lin b) (tetr)tr. Py c) (Trig bi)ss d) (oh)oh e) (tetr)tetr f) (lin)lin 22 a) (Tetra) Trig. Pyramid b) (Trig planar), Trig pl c) (Tr. Bipy) T d) (Tetra) Tetra e) (Trig Bipy) lin f) (Tetra) Bent 24 a) i) Octa (sq.planar) ii) Tetrahedral iii) Trig Bipyr.(see-saw) b) i) Two ii) O iii) One c) S or Se d) Xe 26. a) 104.5o, 120o b) 109.5o, 120o o o c) 107 , 104.5 d) 180o, 109.5o o 28. 2 LP (NH2 , ~109 ), 1 LP (NH3, 107o), 0 LP (NH4+, 109o) 30. a) ClO2- (~109.5o, 2LP) NO2- (120o, 1 LP) b) XeF2 (4 LP around the center) 32. a) Lone Pair on P b) Lone Pair on center O 36. Polar = (b), (c), (e) 38.Ortho and meta 44. Not enough p suborbitals 46. SF2 = sp3, SF4 = sp3d 48. a) sp3 b) sp c) sp2 d) sp3d e) sp3d2 52. b) N2H4 (sp3), N2 (sp) c) N2 stronger bond 54. a) sp3 (C-H), sp2 (C-O) b) 36 ve c) 26 ved) 2 ve- in double e) 8 ve- in lone pairs 56. a) 1, 120o 2, 120o 3, 105o b) sp2, sp2, sp3 c) 21 bonds 62. 100. In2S (I) [Kr]5s24d10 InS (II) [Kr]5s14d10 In2S3 (III) [Kr]4d10 In(III) is smallest (least mutual electron repul) In(III) has the highest lattice energy 102.a) C2H3Cl3O2 b) C2H3Cl3O2 c) Structure CCl3CH(OH)2 11