8.3-Molecular Geometry
advertisement
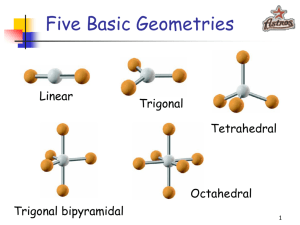
-Understand how the absence or presence of lone pairs of electrons affects the geometry of a molecule -Know what the various geometries are and how to predict them -Understand the concept of orbital hybridization and how it changes the bonding in an atom such as carbon (NEXT LECTURE) The arrangement of atoms within a given molecule. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion = VSEPR ( Section 8.3 232-236 in your textbook) Assumption: Electron pairs repulse each other Consequences 1) This repulsion of electron pairs causes them to orientate as far from each other as possible. 2) Atom centers also want to be as far apart as possible 2 Bonding pairs 0 lone pairs AX2 .. 2 Bonding pairs 2 lone pairs :AX2: 3 Bonding Pairs 0 lone pairs AX3 3 bonding pairs One lone pair :AX3 4 bonding pairs 0 lone pairs AX4 Summary of Five Main Geometries Linear Bent Trigonal Planar Trigonal Pyramidal Tetrahedral Formula= AX2 Formula = : AX2 : Formula = AX3 Formula = : AX3 Formula = AX4 Note: A –represents the central atom X – represents the attached atom • 5 cards in your packet … one for each geometry. • As a group, use your whiteboards to draw the Lewis dot structure for each one of your compound cards. • Once you have the Lewis Dot structure, use it as a guide to construct a model of the compound. • I will walk around and check your Lewis Dot structures and models. • Create a group sheet to record those Lewis Dot structures/models that you are having trouble with. • We will have cool down that you will hand in today (exit slip) Groupwork norm I will also be assessing …. Every student contributes when every student feels safe to make mistakes in the group. What the fudge?! DON’T JUDGE! Hybridization The electron structure of a carbon atom can be written as: Based on this model, we would predict that carbon atoms should form two covalent bonds??!! Instead carbon atoms almost always form 4 bonds. Why???? Hybridization Regular Carbon Aufbau Diagram Hybridized Carbon Aufbau Diagram hybridization 1 s + 3 p = 4 sp3 (All 4 orbitals are now equal at the 2nd energy level) Electrons must be distributed among the new orbitals. Since these hybrid orbitals are equal in energy, the electrons must distributed according to Hund’s Rule. 4 3 sp orbitals 4 sp3 orbitals bond with 4 hydrogen atoms - methane Overlap here is known as sigma bond sp3 carbon 2 sp hybridization 2 sp hybridization carbon double bond - ethene sp hybridization sp hybridization carbon triple bond - acetylene sp hybridization carbon triple bond - acetylene 234-236 in your text discusses these examples