Metals, Metalloids and Non
advertisement

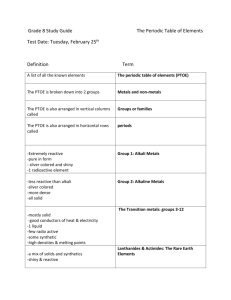
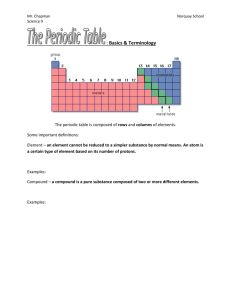
Metals, Metalloids and Non-Metals The periodic table cannot only be divided into families but it can also be organized into four groupings. As the table illustrates, members of the groupings share many properties. Grouping Metals Examples Location Alkali metals, alkaline With exception of H earth and metalloids, all metals, elements to the LEFT transition of staircase. metals(Sc, Ti, V etc) Physical Properties good conductors of electricity and heat; shiny, malleable, usually high density and high melting ,except for alkalis; many react with acid Metalloids With exception of Al, B, Si, Ge, elements that border semi-conductors; some shiny; don't react As, Sb, Te, the staircase (jagged with acid; not malleable Po: line in periodic table) Nonmetals With exception of N, O, S, P, poor conductors of heat and electricity; metalloids and noble Cl, Br, Se low-melting; react with metals and nongases, elements to the etc metals. right of the staircase. He, Ne, Ar, Noble Gases Kr, xe, Rn Last column of the periodic family All gases at room temperature; poor conductors of heat and electricity generally unreactive