Study Guide Chemistry: Remember to Study all Notes and
advertisement

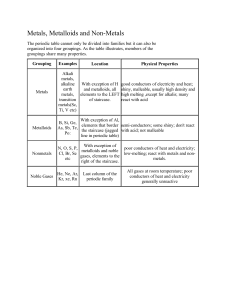
Study Guide Chemistry: Remember to Study all Notes and worksheets given. This is just a study guide. All covered is fair game on the test. Physical/Chemical Changes 1. Iron rusts 2. A cube of ice melts to form a puddle of water 3. Vinegar and baking soda react 4. A chocolate bar melts in the sun Number of atoms and elements in compound 1. NaCl 2. H2O2 3. H3PO4 4. K2CO3 14 Si 28.086 Silicon Atomic Number: equals number of protons Number of Protons = Number of electrons Mass Number: Protons + Neutrons Element Atomic Number Mass Number Mg F S Be Define: 1. Element: 2. Substance: 3. Particles (atoms): 4. Matter: 5. Chemical Reaction: 6. Mendeleev: 7. Periodic Table: 8. Compounds: 9. Physical Properties: 10. Chemical Properties: Periodic Table: How is the Periodic Table organized? What are families (groups) on the periodic table? Notes on Periodic Table: Metals: 1. Make up most of the periodic table Protons Neutrons Electrons 2. Metals are found on the left side of the staircase line that runs through the table. 3. Metals have common physical properties: good conductors, malleable, ductile, shiny, opaque (can’t see through them), solid at room temp. 4. Metals have common chemical properties: reactivity (metals corrode when exposed to water and air) example: rust Malleable: can be hammered into thin sheets Ductile: can be stretched into wire Conductor: easily transfers heat and electricity Reactivity: describes how likely an element is to form bonds with other elements Nonmetals: 1. 2. 3. 4. 2nd largest group of elements on the periodic table. Nonmetals are found to the right of the staircase There are 18 naturally occurring nonmetals Physical Properties: Poor Conductors, brittle, transparent (see through them), dull (gases and solids) Metalloids: 1. The elements that are on the staircase/jagged line 2. Elements that have some properties of both metals and nonmetals Properties of elemental Families: Group 1 (alkali family): Most reactive, soft metals, can be cut with a knife, good conductors. Reactive with water. Group 2 (alkaline earth): very reactive metals. Harder than alkali family. Conductors, ductile, malleable, have a silvery luster. Group 17 (halogens): most reactive nonmetal. Group 18 (noble gases): least reactive of all elements. Gases at room temp. Inert gas family (rare for them to react or bond with any other elements). Very safe to use. Conservation of Mass: 4Fe + 3O2 2Fe2O3 20g 32 g ? What group is the reactants? Products? How much Fe2O3 will be produce? What’s does the phrase mean “conservation of mass”? Particles: How are particles organized in each phase of matter? How do particles move when energy is added? When energy is taken away? When compressed? When expanded?