Physical Properties Notes PPT
advertisement

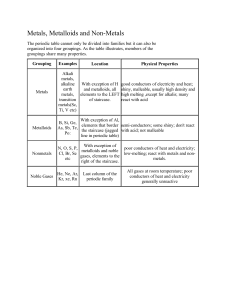
Physical Properties Notes (6.6) The student knows matter has physical properties that can be used for classification. • Compare metals, nonmetals, and metalloids using physical properties such as luster, conductivity, or malleability Physical Properties • Appearance – Color, size, shape, texture • Buoyancy – Tendency to float • Boiling Point – Temp where it changes from liquid to gas • Conductivity – Ability to conduct heat, sound or electricity • Density –Amount of matter in a given volume D=m/v • Ductility – Ability of a substance to be pulled into a thin strand, such as wire. • Hardness – Ability to resist being scratched • Luster- How it reflects light • Magnetism – Ability to attract iron • Malleability – Ability to be pressed or pounded into thin sheets • Mass – Amount of matter in an object • Melting point – Temp where a substance changes from a solid to a liquid. • Odor • Solubility – Ability of a substance to dissolve • State of Matter – Solid, liquid or gas • Temperature – Amount of energy in matter • Volume – Amount of space an object takes up. Metals, Nonmetals, & Metalloids • Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids based on their properties. • Metal – element that is shiny, ductile, malleable and a good conductor • Nonmetal- element that is not shiny, ductile, malleable and is not a good conductor • Metalloid – an element that has properties of both metals and non metals. • Zig zag line (stair step) on periodic table separates the metals and nonmetals • 6 elements that border the zig zag are metalloids http://www.cwu.edu/~cots/images/periodic_table.jpg Metals Non metals Metalloids Shiny Mostly dull Varying ability to conduct electricity Malleable (can be flattened into sheets) Brittle, not malleable or ductile Can be used to make semiconductors – conduct electricity only under certain conditions. Ductile (can be shaped into wires) Poor conductors of heat & electricity Good conductors of heat & electricity Many are gases at room temp. Most are solid at room temp.