Chapter 13
advertisement

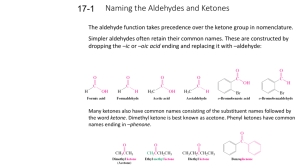
Denniston, 7 Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Thirteen acetal (13.4) the family of organic compounds formed via the reaction of two molecules of alcohol with an aldehyde in the presence of an acid catalyst. addition reaction (13.4) a reaction in which two molecules add together to form a new molecule; often involves the addition of one molecule to a double or triple bond in an unsaturated molecule; e.g., the addition of alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone to form a hemiacetal or hemiketal. aldehyde (13.1) a class of organic molecules characterized by a carbonyl group; the carbonyl carbon is bonded to a hydrogen atom and to another hydrogen or an alkyl or aryl group. aldol condensation (13.4) a reaction in which aldehydes or ketones react to form a larger molecule. Benedict’s Test (13.4) a test reagent used to distinguish aldehydes and ketones; a test for reducing sugars. carbonyl group (Intro) the functional group that contains a carbon-oxygen double bond; -C=O; the functional group found in aldehydes and ketones. hemiacetal (13.4) the family of organic compounds formed via the reaction of one molecule of an alcohol with an aldehyde in the presence of an acid catalyst. hemiketal (13.4) the family of organic compounds formed via the reaction of one molecule of alcohol with a ketone in the presence of an acid catalyst. hydrogenation (13.4) a reaction in which hydrogen (H2) is added to a double or a triple bond. ketal (13.4) the family of organic compounds formed via the reaction of two molecules of alcohol with a ketone in the presence of an acid catalyst. ketone (13.1) a family of organic molecules characterized by a carbonyl group; the carbonyl carbon is bonded to two alkyl groups, two aryl groups, or one alkyl and one aryl group. oxidation (of carbonyl compounds) (13.4) the loss of electrons by a molecule, ion, or atom; in organic compounds, it can be recognized by the gain of oxygen or the loss of hydrogen; e.g., the conversion of an alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone via the use of an oxidizing agent. Tollens’ Test (13.4) a test reagent (silver nitrate in ammonium hydroxide) used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones; also called the Tollens’ silver mirror test.