Chemistry of Cooking & Oxidation: Answer Key
advertisement
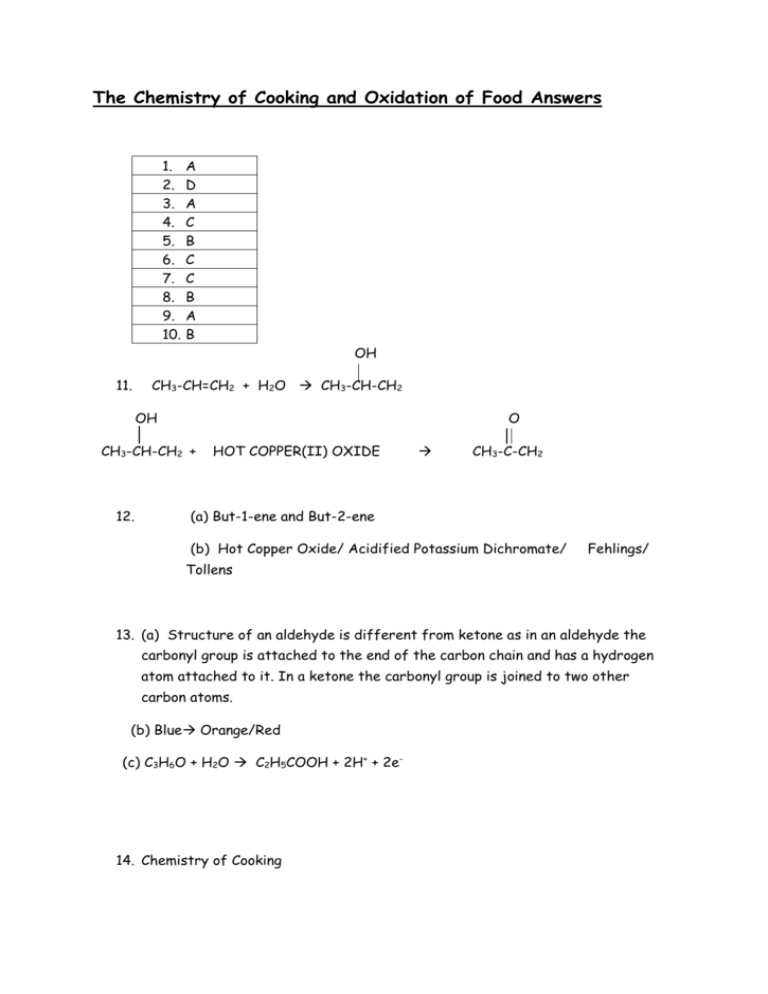
The Chemistry of Cooking and Oxidation of Food Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. A D A C B C C B A B OH 11. CH3-CH=CH2 + H2O CH3-CH-CH2 OH O CH3-CH-CH2 + 12. HOT COPPER(II) OXIDE CH3-C-CH2 (a) But-1-ene and But-2-ene (b) Hot Copper Oxide/ Acidified Potassium Dichromate/ Fehlings/ Tollens 13. (a) Structure of an aldehyde is different from ketone as in an aldehyde the carbonyl group is attached to the end of the carbon chain and has a hydrogen atom attached to it. In a ketone the carbonyl group is joined to two other carbon atoms. (b) Blue Orange/Red (c) C3H6O + H2O C2H5COOH + 2H+ + 2e- 14. Chemistry of Cooking 15. (a) Aldehydes (b) 4-methyl pent-2-ene 16. (a) Oxidation (b) 8 (c) Lemon juice contains lots of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) This is an antioxidant and so will readily undergo oxidation thus saving the fruit from being oxidised. 17. (a) Hydration (b) 18. (a) Furaneol is soluble in water due to the polar OH group being able to make bonds with the water molecules. Capasicin is insoluble due to it being non-polar (amide group on long hydrocarbon chain) (b) Milk contains natural emulsifiers.