The four major operations a computer performs are as follows:
advertisement
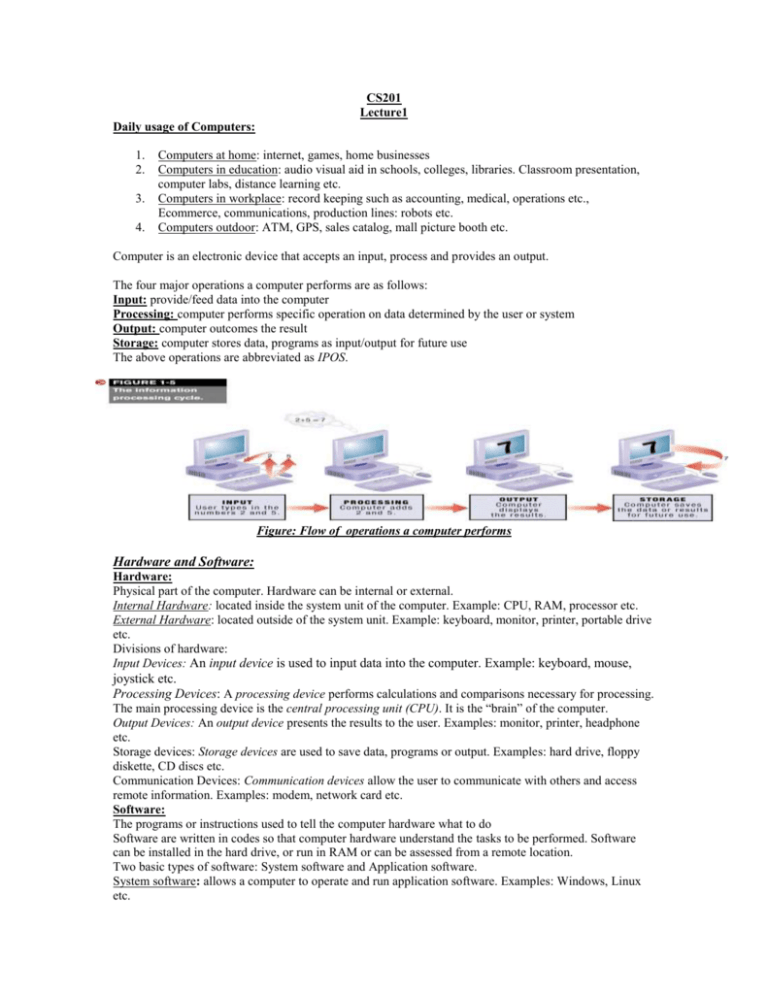
CS201 Lecture1 Daily usage of Computers: 1. 2. 3. 4. Computers at home: internet, games, home businesses Computers in education: audio visual aid in schools, colleges, libraries. Classroom presentation, computer labs, distance learning etc. Computers in workplace: record keeping such as accounting, medical, operations etc., Ecommerce, communications, production lines: robots etc. Computers outdoor: ATM, GPS, sales catalog, mall picture booth etc. Computer is an electronic device that accepts an input, process and provides an output. The four major operations a computer performs are as follows: Input: provide/feed data into the computer Processing: computer performs specific operation on data determined by the user or system Output: computer outcomes the result Storage: computer stores data, programs as input/output for future use The above operations are abbreviated as IPOS. Figure: Flow of operations a computer performs Hardware and Software: Hardware: Physical part of the computer. Hardware can be internal or external. Internal Hardware: located inside the system unit of the computer. Example: CPU, RAM, processor etc. External Hardware: located outside of the system unit. Example: keyboard, monitor, printer, portable drive etc. Divisions of hardware: Input Devices: An input device is used to input data into the computer. Example: keyboard, mouse, joystick etc. Processing Devices: A processing device performs calculations and comparisons necessary for processing. The main processing device is the central processing unit (CPU). It is the “brain” of the computer. Output Devices: An output device presents the results to the user. Examples: monitor, printer, headphone etc. Storage devices: Storage devices are used to save data, programs or output. Examples: hard drive, floppy diskette, CD discs etc. Communication Devices: Communication devices allow the user to communicate with others and access remote information. Examples: modem, network card etc. Software: The programs or instructions used to tell the computer hardware what to do Software are written in codes so that computer hardware understand the tasks to be performed. Software can be installed in the hard drive, or run in RAM or can be assessed from a remote location. Two basic types of software: System software and Application software. System software: allows a computer to operate and run application software. Examples: Windows, Linux etc. Application software: performs specific tasks or applications. Example: customized software, MS Office, games, Real Player etc. Data = raw, unorganized facts. Can be in the form of text, graphics, audio, or video. Information = data that has been processed into a useful form Information processing: conversion of data to information Computer users or end users: are the people who use a computer to obtain information Programmers: are computer professionals whose job it is to write the programs that computers use Networks and Internet: A computer network links computers together so that users can share hardware, software, and data, as well as electronically communicate with each other. Network uses a network server to manage the data flowing through the network devices. Server: A server is a powerful computer in the network that serves clients in terms of providing access, sharing devices within the network. Client: Clients are computers on the network that access resources via the network server Examples of network: home network, computer lab network, office network, network across states etc. Thin client: Uses server’s disk drive for storage and CPU for processing. Advantage: Low cost. Disadvantage: Limited storage and slow rate of processing. Internet: History of internet: ARPANET 1956: US Govt. funded to create ARPA under Defense Department 1969: Four universities were connected through Packet Switching Network. It used Net Control Protocol. 1971: Creation of Email NCP became insufficient so TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) was introduced 1983:TCPIP used to connected to Internet NFS Net 1993: NFS became Internet 1993: Creation of URL, First graphic browser UserISPBackboneAccess PointBackboneISPUser Figure: Internet Connection Today to make the internet more efficient there are Mini NAPSInter connected backbone To access network: Need a modem or network adapter to connect to the network. Need software (often built into the operating system) allows you to log on to the network and access resources. Need an ISP and Web browser to access Internet resources. Need user ID and password to log on to the network. Five basic categories of computers: Mobile devices: Examples: PDA Personal computers: Example: Desktop PC, Notebook computers or laptop Midrange servers: Fall between microcomputers and mainframes in processing power. Used in small network Mainframe computers: Standard choice for most large organizations. Specialize in high-volume processing power Supercomputers: Used for applications that have extraordinary demands for processing power. Offer very fast speeds and extreme degrees of accuracy