Molecular Polarity Lab: Understanding Intermolecular Forces
advertisement

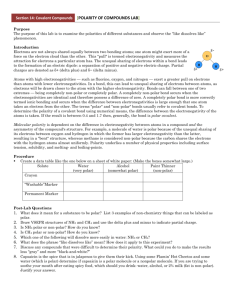
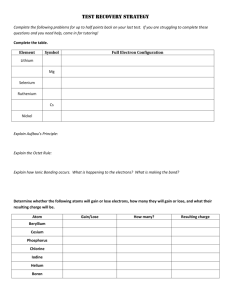
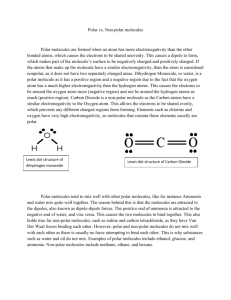
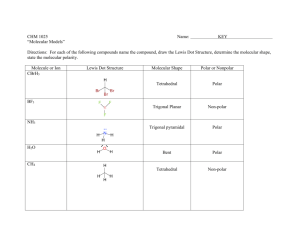
Section 21: Molecular Polarity and Intermolecular Forces [POLARITY OF COMPOUNDS LAB] Purpose The purpose of this lab is to examine the polarities of different substances and observe the “like dissolves like” phenomenon. Introduction Electrons are not always shared equally between two bonding atoms; one atom might exert more of a force on the electron cloud than the other. This "pull" is termed electronegativity and measures the attraction for electrons a particular atom has. The unequal sharing of electrons within a bond leads to the formation of an electric dipole: a separation of positive and negative electric charge. Partial charges are denoted as δ+ (delta plus) and δ− (delta minus). Atoms with high electronegativities — such as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen — exert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities. In a bond, this can lead to unequal sharing of electrons between atoms, as electrons will be drawn closer to the atom with the higher electronegativity. Bonds can fall between one of two extremes — being completely non-polar or completely polar. A completely non-polar bond occurs when the electronegativities are identical and therefore possess a difference of zero. A completely polar bond is more correctly termed ionic bonding and occurs when the difference between electronegativities is large enough that one atom takes an electron from the other. The terms "polar" and "non-polar" bonds usually refer to covalent bonds. To determine the polarity of a covalent bond using numerical means, the difference between the electronegativity of the atoms is taken. If the result is between 0.4 and 1.7 then, generally, the bond is polar covalent. Molecular polarity is dependent on the difference in electronegativity between atoms in a compound and the asymmetry of the compound's structure. For example, a molecule of water is polar because of the unequal sharing of its electrons between oxygen and hydrogen in which the former has larger electronegativity than the latter, resulting in a "bent" structure, whereas methane is considered non-polar because the carbon shares the electrons with the hydrogen atoms almost uniformly. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting- and boiling-points. Procedure Create a data table like the one below on a sheet of white paper: (Make the boxes somewhat large and square.) Solute Water Alcohol Paint Thinner (very polar) (somewhat polar) (non-polar) Crayon “Washable”Marker Permanent Marker Using your crayon, color in the three boxes in the crayon row on your sheet of white paper. Repeat with the washable marker and the permanent marker. Dip a q-tip in water and rub the water end on the square that has the crayon in it. Using the other side of the qtip dipped in water; rub on the square with the washable marker in it. Finally, using a different q-tip dipped in water, rub the water end in the square with the permanent marker. Repeat using a different end of the q-tip each time with both alcohol and paint thinner. Post-Lab Questions 1. What does it mean for a substance to be polar? List 3 examples of non-chemistry things that can be labeled as polar. 2. Draw VSEPR structures of NH3 and CH4 and use the delta plus and minus to indicate partial charge. Is NH3 polar or non-polar? How do you know? Is CH4 polar or non-polar? How do you know? 3. Which one of the following will dissolve more easily in water: NH 3 or CH4? 4. What do you think the phrase “like dissolves like” mean? How does it apply to this experiment? 5. Capsaicin is a large, non-polar spice that is in jalapenos to give them their kick. If you are trying to soothe your mouth after eating spicy food, which should you drink: water, alcohol, or 2% milk (fat is non-polar). Justify your answer.







![QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619037_1-3340fd6e4f1f4575c6d8cf5f79f0ff3e-300x300.png)