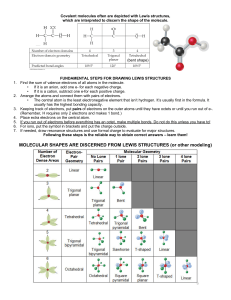
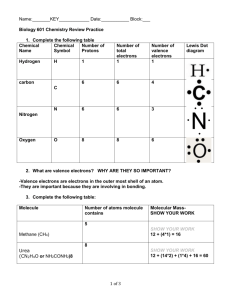
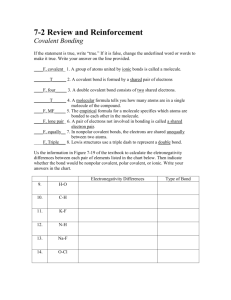
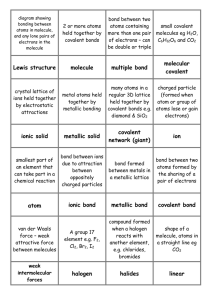
QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3
advertisement
![QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619037_1-3340fd6e4f1f4575c6d8cf5f79f0ff3e-768x994.png)
QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name:________________________________[7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3 problem-solving strategies from last week [25 pts] 2.) Circle and label the atoms that are hydrogen bond (interactions) DONORS and ACCEPTORS in the following molecule [18 pts] (+ 3pts for correct, - 3pts for incorrect) I’ll talk about this in class – overlaying circles and labeling things on this image in Word is a nightmare… 3.) Match the word to its definition bellow. THERE ARE MORE WORDS THAN DEFINITIONS [20pts] covalent nucleotide ionic electronegativity polar amino acid nucleic acid purine ____ covalent _Referring to a stable bonding interaction between atoms; a simple covalent bond is the result of equal or unequal sharing of an electron pair, with each atom contributing one electron in the pair. ___ ionic __ Referring to a molecule or atom that has a negative or positive charge due to a gain or loss of electrons. __ electronegativity _An atomic property reflecting the “desire” or “covetousness” of atoms for electrons (both their own and those of others). Comparison of this property allows one to predict whether two atoms will share electrons equally, unequally, or one will lose and the other gain the electrons altogether. _ nucleotide _The ready-to-install state of a unit of DNA or RNA; it contains the base (the “identity” part), a sugar (formally a “ribose”) and a string of phosphates. _ polar Having an unequal distribution of charge, such as an O–H bond wherein the oxygen is partially negatively charged and the hydrogen partially positively charged. 4.) Explain WHY “oil and water don’t mix”. [30 pts] Your answer should incorporate the concept of electronegativity Write it as if I (Emily) don’t understand anything, i.e. define/explain all technical terms/jargon Oil and water do not mix because they have fundamentally different characteristics. Water is a polar molecule, meaning that it has a region that is partially positively charged and a region that is partially negatively charged. This is due to the fact that O is more electronegative (has more of a ‘desire’ for electrons) than H. Because O ends up ‘spending more time’ with the electrons that make up the covalent bond between the O and the H, it has a partial negative charge, whereas the H has a partial positive charge. Conversely, oil is made up predominantly of Carbons and Hydrogens. Carbon and Hydrogen have roughly equal electronegativities, which mean they share the electrons that make up the covalent bond between them equally, so there is no unevenness of charge on the oil molecule and it ends up being neutral or non-charged (greasy). A polar (molecule with partial (+) and partial (-) regions) water molecule would ‘rather’ interact with another polar water molecule than with the non-polar/uncharged oil molecule, so the oil molecules are ‘corralled’ into one spot because this enables more of the water molecules to interact with other water molecules as opposed to water having to interact with oil molecules.