Kingdoms of Life: Classification Systems Explained
advertisement
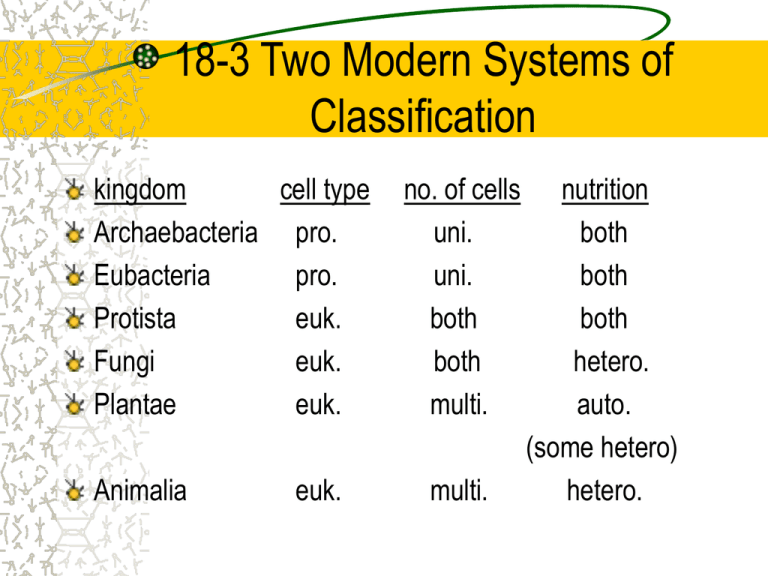
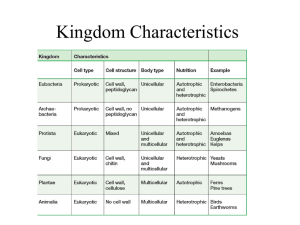
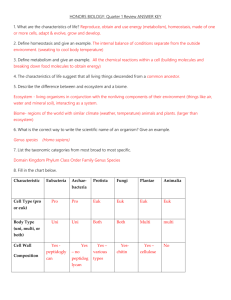
18-3 Two Modern Systems of Classification kingdom cell type Archaebacteria pro. Eubacteria pro. Protista euk. Fungi euk. Plantae euk. Animalia euk. no. of cells uni. uni. both both multi. multi. nutrition both both both hetero. auto. (some hetero) hetero. Prokaryotic = pro. Eukaryotic = euk. Unicellular = uni. Multicellular = multi. Heterotrophy = hetero. Autotrophy = auto. 1. Kingdom Archaebacteria “Ancient bacteria” chemosynthetic bacteria. Live in harsh environments: sulfurous hot springs, very salty lakes, intestines of mammals. Resembles first kinds of organisms to live on Earth. 2. Kingdom Eubacteria “True bacteria” use oxygen. Do not live in harsh environments. Cause tooth decay, milk to turn into yogurt, food poisoning, other disease causing bacteria. Along with kingdom archaebacteria, these include greatest number of living things on Earth. 3. Kingdom Protista Mostly unicellular Giant kelp is multicellular but it lacks specialized tissues (which plants have) 50,000 species euglena, amoeba, paramecium and algae 4. Kingdom Fungi Absorb nutrients (do not ingest) 100,000 species mushrooms, puffballs, molds, mildews, rusts and smuts 5. Kingdom Plantae Most photosynthesize Most on land 350,000 species mosses, ferns, conifers and flowering plants 6. Kingdom Animalia Symmetrical body organization Move about their environment Humans, insects, reptiles, amphibians, birds 3-Domain System Used in modern science. Based on differences of RNA. Domain Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protists Fungi Plantae Animalia