Classification Lecture
advertisement

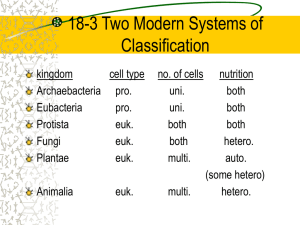
Classification & the New Taxonomy 2010-2011 Chapters 25 – 35 New songs! • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dnF_UdP bJZ0 • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gj15UF08 lUI What determines life? • There are 6 characteristics of life: – Organization – Metabolism – Homeostasis – Growth and Development – Reproduction – Adaptations Solar System Finding commonality in variety • Organisms classified from most general group, domain, down to most specific, species – domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species Earth No. America U. S. N. Y. L. I. Nassau Co. use the mnemonic! Levittown Eukaryote Classification • Old 5 Kingdom system Prokaryote • Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals • New 3 Domain system – reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence • Prokaryote: Bacteria • Prokaryote: Archaebacteria • Eukaryotes – Protists – Plants – Fungi – Animals Archaebacteria & Bacteria Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Kingdom Protist Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plant Kingdom Animal Binomial Nomenclature • Was established in the 18th century by Carlus Linnaeus • Based on structural features as opposed to habitat, size etc. • He used genus which acted as a noun telling what it was • He also used species name which was an adjective to describe the genus Taxon • Term used for the hierarchical classification groups • The smaller the taxon the more similar the organisms within it The Evolutionary Perspective Kingdoms Fungi absorptive nutrition Animalia ingestive nutrition Plantae autotrophs Protista uni- to multicellular Eubacteria multicellular Archaebacteria prokaryotes Single-celled ancestor eukaryotes heterotrophs Bozeman • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wGVgIcT pZkk Why are common names bad? • The classification system makes it easier and quicker to locate different species • There is a uniform Latin language used so it doesn’t have to be translated between languages. It makes it easier for scientists of the world to share information. • It avoids the confusion of common names. For example Ragwort is 2 different plants on PEI and outwest (PEI’s is poisonous) • Puma, Mountain Lion, and Cougar are all the same animals but named different things in different countries Dichotomous Keys • Dichotomous means divided into two parts therefore these keys always give 2 choices in each step. • Sheet Evidences for Classification 1. Fossil Record: radiocarbon dating Evolution of birds • Archaeopteryx – lived about 150 mya – links reptiles & birds Smithsonian Museum, Washington, DC 2006 Fossil Discovery of Early Tetrapod • Tiktaalik – “missing link” from sea to land animals 2. Anatomical record • Homologous structures – similarities in characteristics resulting from common ancestry Homologous structures • • • • Similar structure Similar development Different functions Evidence of close evolutionary relationship – recent common ancestor 3. Comparative embryology • Similar embryological development in closely related species – all vertebrate embryos have similar structures at different stages of development • gill pouch in fish, frog, snake, birds, human, etc. 4. Molecular record • Comparing DNA & Biochemistry (blood, protein, hormones) – universal genetic code! Why compare these genes? • DNA & RNA – compare common genes • cytochrome C (respiration) • hemoglobin (gas exchange) Human/kangaroo 100 DNA & proteins are a molecular record of evolutionary relationships 75 Nucleotide substitutions Closely related species have sequences that are more similar than distantly related species Dog/ cow Human/ cow Rabbit/ rodent Llama/ cow Horse/ donkey 50 Horse/cow Sheep/ goat 25 Human/rodent Pig/ cow Goat/cow 0 0 25 50 75 Millions of years ago 100 125 5. Behaviour • Song Bird: birds that have the same song would be classified more closely 6. Cell Structures • Peptidoglycan = bacteria in cell wall Phylogeny • Evolutionary history of an organism • We often use cladograms to show this history and relationship to other living things • Like a tree the organisms at the top are the most recent Comparative hemoglobin structure Human Macaque Dog Bird Frog 32 45 67 Lamprey Why does comparing amino acid sequence measure evolutionary relationships? 8 125 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Number of amino acid differences between hemoglobin (146 aa) of vertebrate species and that of humans Book Examples • Pg. 115 Horseshoe crab reclassified • Interesting chart on pg. 119