Six Kingdoms
advertisement

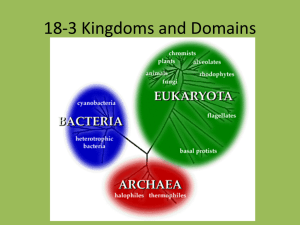
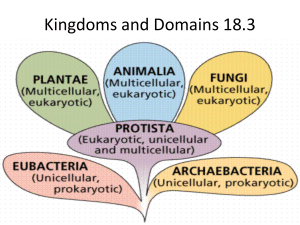
Six Kingdoms-Taxonomy S7L1b Classify organisms based on physical characteristics using a dichotomous key of the six kingdom system (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protist, fungi, plants, and animals). Current Version of the Hierarchy of Living Things • Super kingdom is the broadest category and includes the prokaryotes and the eukaryotes. • Prokaryotes – microscopic unicellular organisms – few organelles – no nucleus. – Mostly photosynthesizers or decomposers – Some are pathogens • Disease-causing – Further divided into two kingdoms • Eubacteria and Archaebacteria Current Version of the Hierarchy of Living Things • Eukaryotes – Unicellular AND multicellular – Divided into four kingdoms • Protista • Fungi • Plantae • Animalia Kingdoms Divide • • • • • • • Kingdom Phylum or divisions Classes Orders Family Genus Species Current system of organization • Carl Linnaeus • Binomial nomenclature • A system of naming organisms using two-part names to label the species • Scientific name – Genus (generic) – Species (specific) – Homo sapiens is the scientific name for humans.