Classification Study Guide: Taxonomy & Kingdoms
advertisement
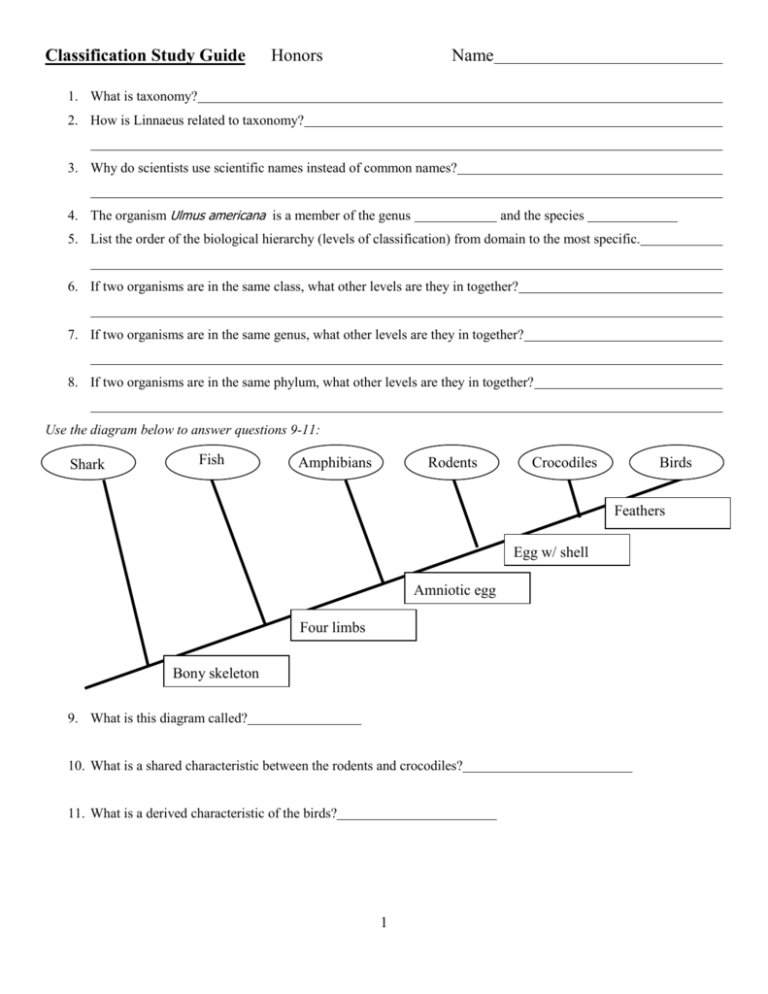
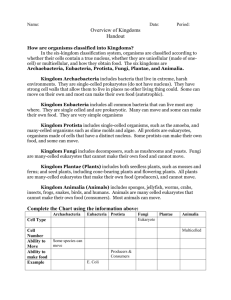
Classification Study Guide Honors Name 1. What is taxonomy? 2. How is Linnaeus related to taxonomy? 3. Why do scientists use scientific names instead of common names? 4. The organism Ulmus americana is a member of the genus and the species 5. List the order of the biological hierarchy (levels of classification) from domain to the most specific. 6. If two organisms are in the same class, what other levels are they in together? 7. If two organisms are in the same genus, what other levels are they in together? 8. If two organisms are in the same phylum, what other levels are they in together? Use the diagram below to answer questions 9-11: Shark Fish Amphibians Rodents Crocodiles Birds Feathers Egg w/ shell Amniotic egg Four limbs Bony skeleton 9. What is this diagram called? 10. What is a shared characteristic between the rodents and crocodiles? 11. What is a derived characteristic of the birds? 1 12. List the major characteristics of the following kingdoms: a. Animalia b. Fungi c. Plantae d. Protista e. Eubacteria f. Archaebacteria (include some potential environments) 13. What is the earliest known group of living organisms on Earth? 14. What characteristics can be used to classify Bacteria? 15. What cell features are found in eukaryotic cells and not prokayotic cells? (include how the shapes of the chromosomes differ) 16. What are the 3 bacterias shapes? 17. What are reasons that viruses could be considered NONLIVING? 18. What is the difference between the lytic and lysogenic cycle of viruses? 19. What are Pseudopodia and what are they used for (based off our project)? 20. What is the difference between an autotroph and a heterotroph? 2 _____________________ 21. What are Algae? 22. What are the similarities between green algae and plants? 23. Biologists hypothesize fungi evolved from what? 24. Chitin is found in which groups organisms? (there are two) 25. What are hyphae? 26. What are mycelium? 27. What organism consists of a fungus and a photosynthetic partner in a symbiotic relationship? 28. Why are Fungi and bacteria important to ecosystems? (what function do they have in common) 29. What are some ways fungi can harm humans? 30. Why are Lichens are important to the environment?__________________________________________________ 31. The ancestors of today’s land plants were probably 32. What challenges were faced by early land plants? 33. The waxy protective covering of a land plant is called a 34. Some land plants developed an internal system of interconnected tubes and vessels called 35. What are the functions of the xylem and phloem? 36. What are the characteristics of nonvascular plants? 37. What are stem or differentiated cells? Cells that specialize and take on specific tasks and their own shapes 38. Animals probably evolved from what? 39. What taxa is considered the “junk-drawer” kingdom? 40. Explain what cladograms and dichotomous keys are and their importance in classifying living things 41-46. Know some examples of species for all six kingdoms. Archaebacteria don’t need to be named, but know where they live. List them below: Archaebacteria Fungi Eubacteria Protista Plantae Animalia 3 47-50. Create a cladogram and a dichotomous key for the 4 plants below. Taxa Characteristics flowers wood and seeds vascular tissue Mosses Ferns Conifers 0 0 0 Flowering Plants 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1A: 1B: 2A: 2B: 3A: 3B: 4