Bacteria - Auburn City Schools
advertisement

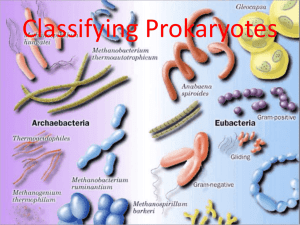
KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA & KINGDOM EUBACTERIA Unit 2 - Biodiversity Bacteria – Prokaryotic Organisms Both kingdoms (Eubacteria and Archaebacteria) were once collectively known as Kingdom Monera. Prokaryotic Means that it doesn’t have a nucleus. A nucleus holds all of a cells DNA, so the DNA in a bacteria cell is just “stuffed” inside the cell, along with free floating ribosomes (which help make proteins and have RNA). Reproduces by binary fission Since the cell’s DNA is not concentrated in one area all the bacteria cell has to do is double it’s genetic material, and split in half. Binary fission – Asexual Reproduction Bacteria – Single Celled Organisms All bacteria cells are unicellular. All the characteristics of life occur in one cell. If lots of cells divide and live in one area (usually cultured on agar) it is called a colony. Kingdom Archaebacteria Differ from Eubacteria in the fact that their RNA (found in ribosomes) is arranged differently and cell walls are different. They are mostly anaerobic (don’t need oxygen) Are found in very harsh environments Very salty, acidic and hot places. Volcanic Vents, Hot springs, bottom of the ocean. Thought to be the oldest living organisms on Earth. It is believed that Earth’s atmosphere began as a mixture of poisonous gases, where only this type of organism could have survived. Kingdom Eubacteria Most common bacteria. Found everywhere All known pathogens (the bacteria that makes you sick) are in K. Eubacteria Also all the good for you bacteria (like in yogurt). Examples include: Streptococcus Clostridium tetani Clostridium botulinum Lactobacillus Pictures – Look alike to me??? I can see why they were once grouped together Archaebacteria Eubacteria Naming Bacteria – What’s your shape? Often bacteria is named for it’s shape and arrangement. Arrangements Shapes (most common) (most common) Strepto (chain) Coccus (sphere shaped) Staphylo (cluster) Bacillus (rod shaped) Diplo (pair) Sprillium (spiral shaped) Bacteria and you – Pros & Cons Positive Contributions Decomposers “Fix” nitrogen into a useable form Food production—yogurt, cheese, etc. Sewage Treatment Clean Oil Spills Source of antibiotics Negative Aspects Disease Syphilis, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, strep throat, botulism, etc. Food Spoilage Resistance to drugs.