Kingdoms Archaebacteria, Eubacteria and Protista
advertisement

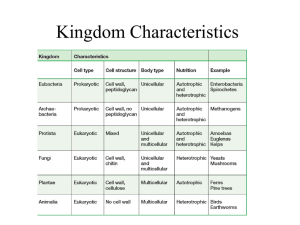
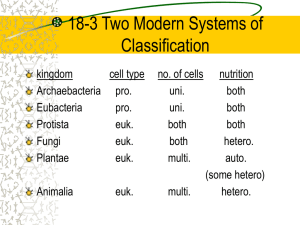
KINGDOMS ARCHAEBACTERIA, EUBACTERIA & PROTISTA I. Superkingdom Prokaryota Superkingdom Prokaryotes = Domain Archaea and Domain Eubacteria = Monerans = “bacteria” A. Characteristics of Prokaryotes 1. Cellular structure a. Most lack nuclear membrane b. Have ribosomes, but most have no other organelles 2. Binary fission (asexual reproduction) - some divide every 20 min. 3. Endospores - survive unfavorable conditions 4. Examples a. Saprophytic decomposers - important in ecosystem recycling b. Anaerobes i. Live in gut / soil ii. Breakdown macromolecules or synthesize molecules used by host iii. Base of foodwebs under anaerobic conditions 5. Metabolic processes utilized a. Fermentation b. Anaerobic electron transport (glycolysis) c. Chemosynthesis B. Domain Archaea consists of the Kingdom Archaebacteria 1. Oldest Kingdom on Earth a. Ancestors of all other organisms on Earth i. One branch evolved to become Eubacteria ii. Another branch evolved to become Protista, and later, the Kingdoms Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia iii. A third branch did not evolve or experienced little change and is represented by modern Archaebacterial species b. Earliest fossils: 3.2-3.8 billion years old 2. Phyla a. Methanogens (produce CH4 as waste product) b. Halophiles c. Extreme thermophiles Chemosynthetic bacteria i. ii. Oxidize inorganic compounds for food Base of foodweb 1.5 miles below ocean surface O2 + 4H2 S + CO2 + geothermal energy (CH2 O)x + 4S + 3H2 O 1 C. Domain Eubacteria (Domain Bacteria) consists of the Kingdom Eubacteria 1. Heterotrophic bacteria a. Shapes i. Coccus (round) ii. Bacillus (rods) iii. Spirillium (spirals) b. Some cause diseases (pathogens) i. Gonorrhea ii. Chlamydias (sexually transmitted urethritis) iii. Syphilis iv. Lyme disease v. Tetanus vi. Anthrax 2. Photosynthetic bacteria = Cyanobacteria = “Blue-green algae” a. Chlorophyll a b. Most likely the organisms that changed the atmosphere from reducing to oxidizing c. Large mats exist in oceans today d. Algal blooms = sign of pollution / danger (cultural eutraphication) nutrients cyanobacteria nutrients cyanobacteria detritus O2 death of fish II. Superkingdom Eukaryota consists of the Domain Eukarya Superkingdom Eukaryota = Domain Eukarya = Kingdom Protista + Kingdom Plantae + Kingdom Fungi + Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Protista (aquatic) A. Protozoa (animal-like protists) 1. Amoebas; move via pseudopods 2. Ciliates 3. Flagellates a. Guiardia b. Red tide and Pfeisteria (dinoflagellates) 4. Sporozoa a. Nonmotile b. ex: 1) malaria (Plasmodium) 2 B. 1. 2. 3. 4. C 2) toxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma) cat feces -- humans (birth defects) Algae (plantlike protists) Green - ancestors of plants ex: sea lettuce Golden-brown diatoms– base of foodweb in most freshwater streams Brown Fucus Sargassum Red - coral-like Euglenoids animal-like motile flexible 2. plant-like photo chloroplasts 1. D. Slime molds & water molds (Fungi-like protists) 1. Slime molds produce windblown spores like fungi ingest food like amoebas 2. Water molds saprophytic, external digestion, & threadlike body like fungi diploid cells (unlike haploid fungi) ex: potato famine (1845 - 1860) III. Distribute handout: "Plant/Animal Evolution" IV. Homework: OUTDOOR LECTURE next session be prepared: Wear appropriate clothing. Bring clipboard. Bring seat cushion. (optional) Bring Evolutionary Tree and Plant/Animal Evolution handout Review the “Evolutionary Tree” Study handout, Plant/Animal Evolution Required and Extra Credit: DUE AT START OF NEXT LECTURE: (see outline of homework for details) 3