Taxonomy - TeacherWeb
advertisement

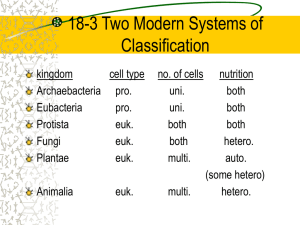
Taxonomy The Science of Organizing and Classifying Life Taxonomy – the science of grouping and naming things. The modern system of classification was developed by Carl Linnaeus in the 1700’s. Carl Linnaeus Born in Sweden in 1707 Developed a system of classifying living organisms into large generalized groups and dividing each group into smaller and smaller specialized groups Linnaeus grouped organisms according to their physical similarities. Linnaeus believed so much in his system, he changed his name to Carolus linnaeus. Taxonomic Categories All living things are grouped in categories progressing from large general groups to smaller and smaller specific groups: 7 Taxonomic Categories: Kingdom (most generalized group) Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species (most specific group) Binomial Nomenclature (Writing Scientific Names) Each organism is given a 2-word name consisting of its genus and species names. The genus name is ALWAYS written first and is capitalized The species name is ALWAYS last and is lower-case Both names are either underlined or italicized. For example: dog = Canis familiaris or Canis familiaris For example: lion = Panthera leo or Panthera leo The 6 Kingdom System Each living organism is classified into one of 6 kingdoms: Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Anamalia Kingdom Archaebacteria Believed to be some of the first living things on the early earth. All prokaryotes Live in extreme environments: Hot thermal springs Extremely acid environments Extremely salty environments Oxygen free environments Kingdom Eubacteria All prokaryotes Eubacteria are ubiquitous. (I.e. they can be found almost everywhere!) Some cause disease, but most are harmless. Kingdom Protista Eukaryotic Mostly single-celled organisms Most require moist envoronments Divided into “animal-like”, “plant-like”, and “fungus-like” groups. Kingdom Fungi Mostly multicellular eukaryotes Obtain nutrients and energy by decomposition (Therefore they are heterotrophic) Have a cell wall made of chitin Reproduce by producing “spores” Kingdom Plantae • All are multicellular photoautotrophs • Classified as simple or complex based on the presence or absence of vascular tissue (xylem & phloem) • Vascular plants are also classified according to wether or not they produce flowers. Kingdom Animalia Animals All are Multicellular. All are heterotrophs. Cells of animals are organized into tissues. Tissues are organized into organs. Organs are organized into organ systems.