Kingdom Characteristics: Archaea to Animalia
advertisement
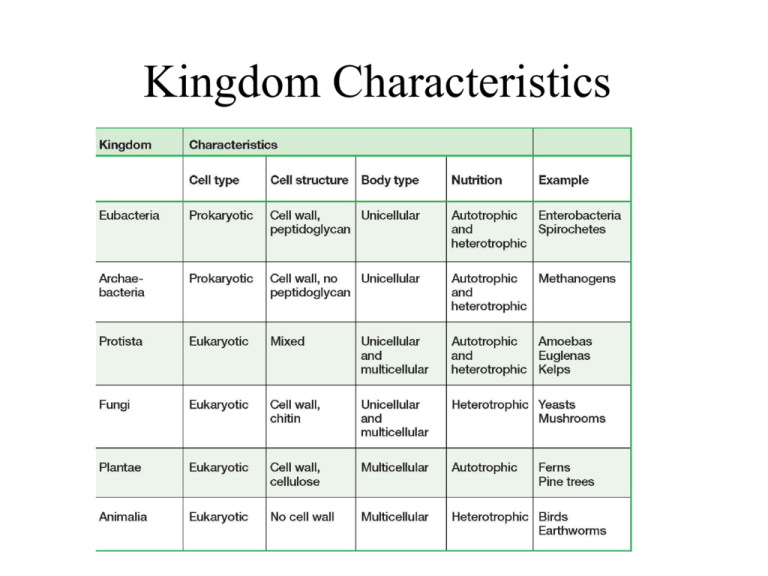
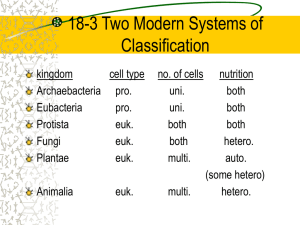
Kingdom Characteristics Kingdoms of Prokaryotic Cells Archaebacteria Eubacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria • Archaea have a chemically unique cell wall and membranes and a unique genetic system. • Scientists think that archaea evolved in a separate lineage from bacteria early in Earth’s history. • Scientists also believe that some archaea eventually gave rise to eukaryotes. • Archaea were first found in extreme environments, such as salt lakes, the deep ocean, or hot springs that exceeded 100°C. • These archaea are called extreme bacteria. • Archaea called methanogens live in oxygenfree environments. Thermophiles live in hot habitats and halophiles in salty areas. Kingdom Eubacteria • True bacteria • Make up normal flora • May be pathogenic such as strept and staph causing skin and throat infections Bacteria reproduce: asexually using binary fission. Conjugation is the Genetic Variation process at which genetic information is passed from one organism to another. Conjugation among bacteria involve the passing of a plasmid from a host bacteria to a recipient bacteria. What is a Plasmid: Extra circular DNA that carries a few extra genes and replicates independently of the host. Bacteria Shapes Kingdoms of Eukaryotic Cells Animalia Plantae Fungi Protista Kingdom Plantae • Almost all plants are autotrophs that produce their own food by absorbing energy and raw materials from the environment. • The process that makes food, photosynthesis, occurs in chloroplasts. • The plant cell wall is made of a rigid material called cellulose. Kingdom Animalia • Animals are multicellular heterotrophs. • Their bodies may be simple collections of cells or complex networks of organ systems. • Animal cells lack a rigid cell wall. Kingdom Fungi • Fungi are heterotrophs that are mostly multicellular. • Their cell wall is made of a rigid material called chitin. • Fungi are considered to be more closely related to animals than to any other kingdom. Kingdom Protista • Kingdom Protista is a “leftover” taxon, so it is a diverse group. • Any eukaryote that is not a plant, animal, or fungi can be called a protist. • Protists did not descend from a single common ancestor. • For many years, biologists recognized four major groups of protists: flagellates, amoebas, algae, and parasitic protists.