Indirect Object Pronouns
advertisement

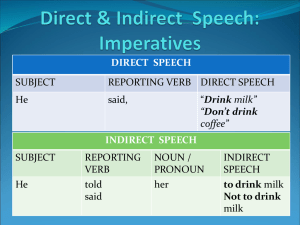
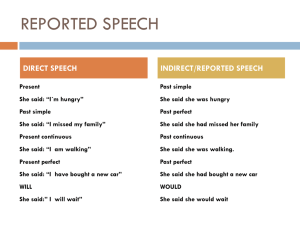
Indirect Object Pronouns Spanish 3 VC c.4 Identifying the parts of a sentence: Verb - the action or state of being Subject – who does the action who or what + verb = subject Direct Object – who or what receives the action directly S+V+ who or what = D.O. Indirect Object – to whom or for whom the action is done S+V+(D.O.) + to whom or for whom=I.O. Identifying an Indirect Object: 1. The I.O. answers the question “to whom?” or “for whom” the action of the verb is performed. S + V + (D.O.) + to whom or for whom = Indirect Object I am giving the gift to her. Object Pronoun Placement 1. If it is the object of a conjugated verb, it goes in front of that verb. 2. If it is the object of an infinitive verb, attach it to the end of the infinitive. Object Pronoun Placement 1. Me gusta la comida china. I like Chinese food. 2. Yo quiero darle el libro a él. I want to give him the book. Object Pronoun Placement 3. Dame el libro. Give me the book. 4. No le dé las llaves a él. Don’t give him the keys. Combination Object Pronoun Placement 1. When more than one object pronoun is used, they need to be placed using the acronym RID (reflexive)(Indirect)(direct) 2. If both the D.O.p and I.O.p are used AND both are in the 3rd person, THEN the I.O.p (le or les) changes to SE Ie…Quiero darselo a ella. Watch for this… • In English the indirect object is typically only represented once, either with the pronoun or the clarifier. Paco gives her the gift. Paco gives the gift to her. Watch for this… • In Spanish the indirect object is typically represented twice, once with the pronoun (manditory) and once with the clarifier (sometimes optional). Paco le da el regalo a ella. Indirect Object Clarifier 1. A 2. Name or prepositional pronoun. mí nosotros ti -----él, ella, Ud. ellos, ellas, Uds. Clarifier Placement 1. Place the indirect object clarifier at the end of the sentence with non-gustar like verbs. 2. Place the I.O. clarifier at the beginning of the sentence with gustar-like verbs. Examples: I.O.c I.O.p V S 1. A Paco le gusta el libro. Paco likes the book. S V I.O.c D.O.n 2. Paco gives her flowers. Paco le da flores a ella. Practice Sentence Translations: 1. Paco invites Marta to his party. 2. Marta gives a present to Paco. 3. The waiter can bring the food to me. 4. Pancho wants to bring the books to us. 5. Pancho is bringing them to us. 6. The waitress is bringing it to me. 7. Are you bringing me a glass of water? 8. He is bringing it to her. 9. Quito is bringing them to Paco. 10. She can bring the ice cream to us. Practice Sentence Translations: 1. Paco invita a Marta a su fiesta. 2. Marta le da un regalo a Paco. 3. El camarero puede traerme la comida. 4. Pancho quiere traernos los libros. 5. Pancho nos los trae. 6. La camarera me lo trae. 7. ¿Me trae Ud. un vaso de aqua? 8. El se lo trae a ella. 9. Quito se los trae a Paco. 10. Ella puede traernos el helado. Turn and with your neighbor compare and contrast indirect objects in Spanish and English.