Notes Unit 7-4 -Lab Reaction rate
advertisement

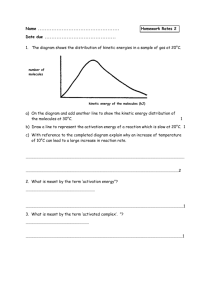
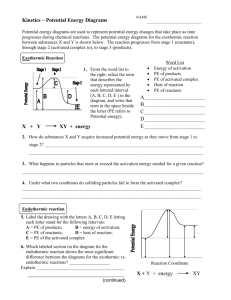
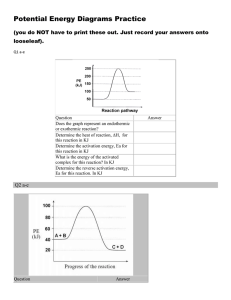
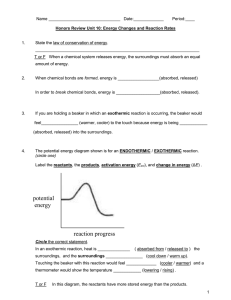
Warm up 2-12-16 1. When do we know that the reaction is complete for a irreversible reaction? 2. What are the four factors that affect the rate of a irreversible reaction? 3. How will the reaction rate change if the temperature went from 30°C to 60°C? 4. What has to happen for a reaction to occur? Agenda Homework -Notes Unit 7-4 -Lab Reaction rate -WS reaction rate Feb 16 - Quiz Feb 16 - Progress report Feb 18 - Extra credit due Notes Unit 7-4 Activation Energy Activation Energy • Activation energy (Ea) - the minimum energy particles must have in order to react • Energy Diagram: Activation Energy Example 1. Find the forward activation energy in (KJ) 2. Find the ΔH Catalysts • Catalysts – Reduces the activation energy so the reaction can happen faster and easier – Catalysts are not used up in a reaction – Enzymes are proteins found in living things that increase reaction rates, a biological catalyst Catalysts Endo Vs. Exothermic Energy • Endothermic Reactions: – Products are at a higher energy than the reactants – Products are less stable – Heat turned into making bonds • Exothermic Reactions: – Products are at a lower energy than the reactants – Products are more stable – Heat go to the environment Check In Exothermic or Endothermic? Check In Exothermic or Endothermic? Lab Reaction Rates • Use the correct graduated cylinder to obtain the solutions • PART 2 DIAGRAM: Graduated Cylinders Thermometer • Get temperature data from other groups Assignments • Notes Summary • Lab reaction rate (due today) • WS reaction rates (due next class) • Quiz Tuesday