12worksheet1.3 - SD43 Teacher Sites
advertisement

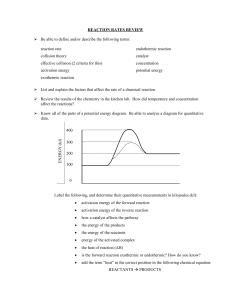
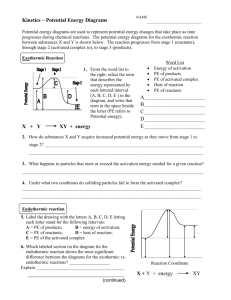
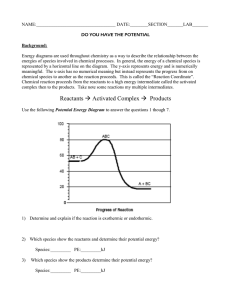
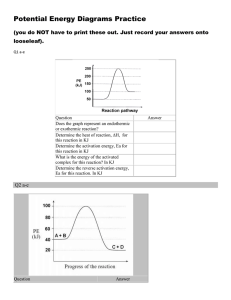
CHEMISTRY 12 WORKSHEET 1.3 Potential Energy Diagrams 1. a) b) c) d) Draw a PE diagram for a fast exothermic reaction Draw a PE diagram for a slow exothermic reaction Draw a PE diagram for a fast endothermic reaction Draw a PE diagram for a slow endothermic reaction 2. If two reactants collide with sufficient KE, are they guaranteed to have an effective collision? 3. As two reactants particles approach each other, what happens to their a) KE and why? b) PE and why? c) total energy before and after the reaction and why? 4. Bond energies for F2 and I2 are almost identical. Would you expect the activation energy for the reaction of fluorine and hydrogen or the reaction of iodine with hydrogen to be greater? (hint: activation energy is the energy to overcome the electron repulsion to make the product as well as the energy to break the bonds to begin.) 5. Draw the following PE diagram. H = -15kJ and Ea(f) = 40 kJ, what is the Ea(r)? 6. Draw the following PE diagram. Ea(r) = 30 kJ and Ea(f) = 55 kJ, what is the H(f)? 7. Draw the following PE diagram. Ea(r) = 10 kJ and Ea(f) = 45 kJ, what is the H(f)? 8. Draw the following PE diagram. Ea(r) = 30 kJ and the reaction is R + 25 kJ P, what is the Ea(f)? 9. Draw the following PE diagram. Potential energy of reactant is 250 kJ, potential energy of activated complex is 350 kJ and the PE of the products is 300 kJ. Is the reaction exo or endothermic, what is the H(r)? 10. Draw the following PE diagram PE of reactants is 350 kJ, activation energy is 100 kJ, PE of products is 250 kJ. What is the H(f) and the P.E. of the activated complex? 11. Draw the following PE diagram. PE of reactants is 100 kJ, PE of activated complex is 400 kJ, H is +150 kJ. What is the Ea (f)? What is the activation energy in the forward direction? If the temperature were increased what would happen to the diagram?