Honors Review Unit 10
advertisement
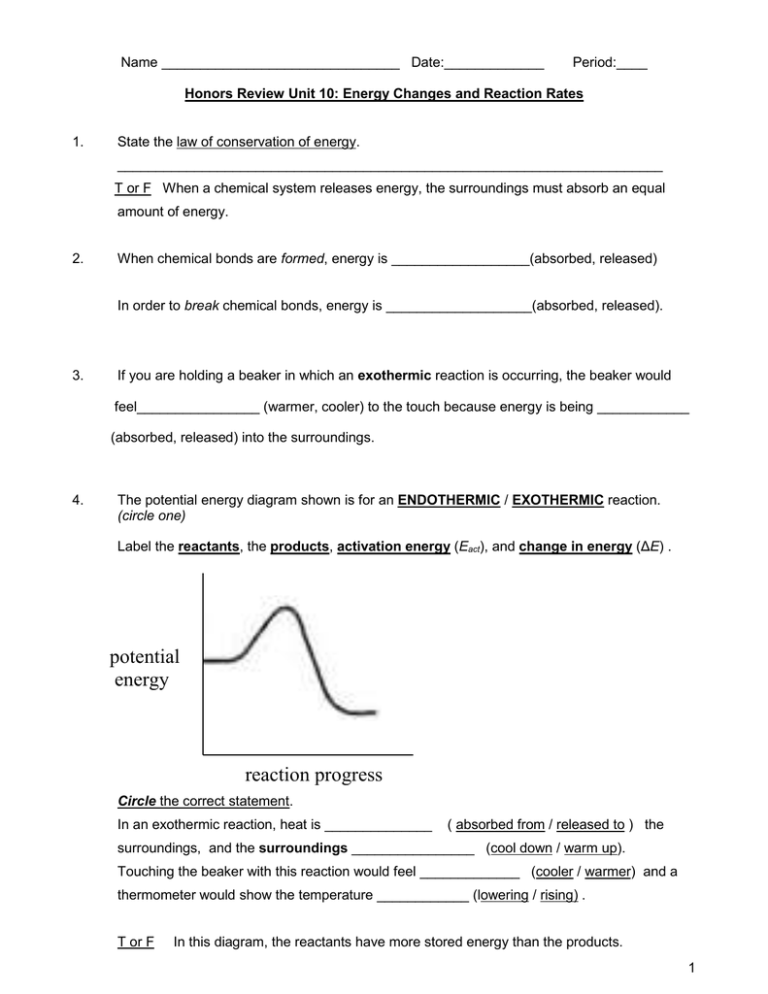
Name _______________________________ Date:_____________ Period:____ Honors Review Unit 10: Energy Changes and Reaction Rates 1. State the law of conservation of energy. _______________________________________________________________________ T or F When a chemical system releases energy, the surroundings must absorb an equal amount of energy. 2. When chemical bonds are formed, energy is __________________(absorbed, released) In order to break chemical bonds, energy is ___________________(absorbed, released). 3. If you are holding a beaker in which an exothermic reaction is occurring, the beaker would feel________________ (warmer, cooler) to the touch because energy is being ____________ (absorbed, released) into the surroundings. 4. The potential energy diagram shown is for an ENDOTHERMIC / EXOTHERMIC reaction. (circle one) Label the reactants, the products, activation energy (Eact), and change in energy (ΔE) . potential energy reaction progress Circle the correct statement. In an exothermic reaction, heat is ______________ ( absorbed from / released to ) the surroundings, and the surroundings ________________ (cool down / warm up). Touching the beaker with this reaction would feel _____________ (cooler / warmer) and a thermometer would show the temperature ____________ (lowering / rising) . T or F In this diagram, the reactants have more stored energy than the products. 1 5. The potential energy diagram is for an ENDOTHERMIC / EXOTHERMIC reaction. (circle one) Label the reactants, the products, activation energy (Eact), and change in energy (ΔE) . potential energy reaction progress Circle the correct statement. In an endothermic reaction, heat is ___________ ( absorbed from / released to) the surroundings, and the surroundings ______________ ( cool down / warm up). Touching the beaker with this reaction would feel ______________ (cooler / warmer) , and a thermometer would show the temperature ______________ ( lowering / rising). T or F In this diagram, the reactants have more stored energy than the products. 6. Define activation energy: ____________________________________________________________ 7. A catalyst is a substance that _________________(increases, decreases) the reaction rate. It works by _________________(raising, lowering) the activation energy for the reaction. 8. T or F Catalysts will be changed in the reaction and can never be reused. 2 reaction progress 9. Consider reactions B and C above. The different heights of reactions B and C represent the _________________________ of the reaction. Reaction ___ is a catalyzed reaction, while Reaction ___ is an uncatalyzed reaction. Reaction B has a _____________ ( lower / higher) activation energy and occurs at a _________ (slower / faster) rate. 10. Circle EACH of the following that could express a reaction rate in amount per time: mol/L g/s s/mol mol/min g/mol 11. T or F Collision theory states that the ONLY requirement needed for a chemical reaction to occur is that the reactant particles must collide. 12. T or F To be effective, a collision requires both the proper orientation of particles and the collisions must occur with sufficient energy to react. 13. How does each factor affect the rate of a reaction? 1) increased concentration effect on rate: increases or decreases 2) increased temperature effect on rate: increases or decreases 3) increased activation energy effect on rate: increases or decreases 4) use of a catalyst effect on rate: increases or decreases 5) increased surface area effect on rate: increases or decreases 3 14. Explain why increasing the concentration of reactants increases the reaction rate. Higher concentrations cause more ________________________ between _____________________. 15. Explain why a reaction rate increases with an increase in temperature. Higher temperatures cause more _______________________ of greater ______________________. 16. Reaction rates increase with ___________ (smaller / larger) particle sizes which provide ________ (less / more) surface area of reactant available for collisions. 17. A catalyst is a substance that _________________(speeds up, slows down) the reaction rate. It works by _________________(raising, lowering ) the activation energy. Catalysts _________ (do, do not) get consumed in the reaction and can be used over again. reaction progress 18. Consider reactions B and C above. Which reaction has a higher activation energy? _________________ Which reaction will be faster? ______________________ 19. Why is it easier to light a pile of sawdust on fire compared to a large log? _____________________________________________________________________________ 20. Consider a candle on a table that burns for 2 hours before going out. Would you classify this system as OPEN, CLOSED, or ISOLATED? Explain. __________________ because _____________________________________________________________________________ 4




