UNIT 11---CHEMICAL REACTIONS

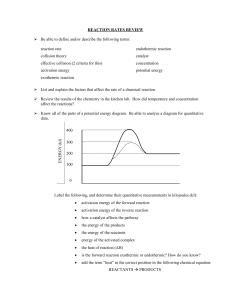
1 What is the collision theory, and how does it relate to reaction rates?
Particles must collide and break the existing bonds so they can form new ones. They need the correct orientation and enough energy.
2 According to the collision theory, what must happen in order for two molecules to react?
Correct orientation & enough energy
3 How is the speed of a chemical reaction related to the nature of the reactants?
(gases) >>> (liquids) >> (solids)
4 How do temperature, concentration, and surface area affect the rate of a chemical reaction
Rate
5 How does the activation energy of an uncatalyzed reaction compare with that of the catalyzed reaction?
Catalyzed = lower activation energy
6 Explain why a crushed solid reacts with a gas more quickly than a large chunk of the same solid.
More exposed surface area
7 What is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the reaction?
Catalyst
8 Explain how a catalyst affects the activation energy for a chemical reaction.
It lowers the activation energy by taking a different pathway
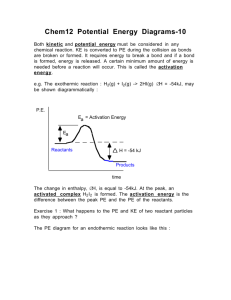
9 Hydrogen bromide is added to a solution of potassium hydrogen carbonate to produce potassium bromide, hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide gas. The temperature of
the solution goes up.
10 Calculate the change in enthalpy of the following reactions
N
2
(g) + 2O
2
(g) → 2NO
2
(g)
+66.2 kJ
4NH
3
(g) + 7O
2
(g) → 4 NO
2
(g) + 6 H
2
O (l)
-1398.98 kJ
10 Calculate the change in enthalpy of the following reactions
2FeCl
2
(s) + Cl
2
(g) 2FeCl
3
(s)
-115.4 kJ
CaCO
3
(s) → CaO(s) + CO
2
(g) +179.001 kJ
11 4Fe + 3O
2
2Fe
2
O
3
+ 1625 kJ
What happens to the change in energy during the previous reaction? A.C.
Heat = product = exothermic
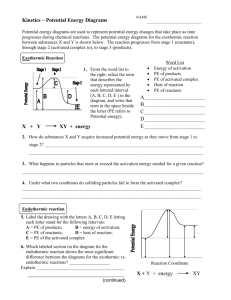
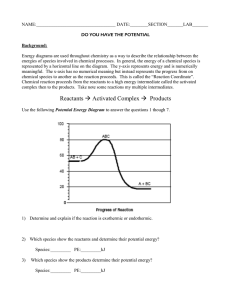
12 Label the reactants, products, and activated complex.
13 Calculate the EA and heat of reaction.
R
P
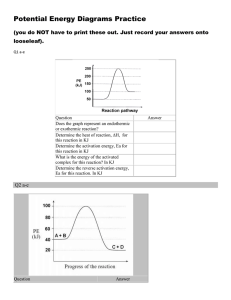
14 Label the reactants, products, and activated complex.
15 Calculate the EA and heat of reaction.
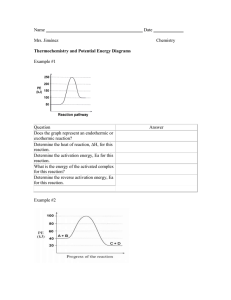
a b c d e f
Potential Energy Diagram Worksheet
1. Which of the letters a–f in the diagram represents the potential energy of the products? e
2. Which letter indicates the potential energy of c
3. Which letter indicates the potential energy of a
4. Which letter indicates the activation energy? b
5. Which letter indicates the heat of reaction? f
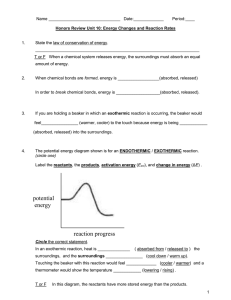
6. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Endo = +
H, products gained E.
7. Which letter indicates the activation energy of d
8. Which letter indicates the heat of reaction of f
9. Is the reverse reaction exothermic or
Exo = -
H
10. Draw an energy diagram for a reaction. (Label the x&y axis)
Potential energy of reactants = 350 kJ/mole
Activation energy = 100 kJ/mole
Potential energy of products = 250 kJ/mole
Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? Exo
What can be added to lower the activation energy?
Catalyst
450 kJ
EA= 450-350=100 kJ
350 kJ
H = Products-reactants=250-350=-100 kJ
250 kJ
Time