Protists - solbergbiology
advertisement

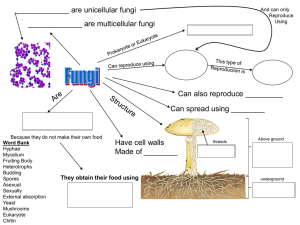
Protists Chapter 19 I. What is a Protist? A. Kingdom Protista is a diverse kingdom, including: 1. single or multi-celled organisms 2. heterotrophs or autotrophs 3. microscopic or large 4. all are eukaryotes B. organisms can be animal like- Protozoa 1. all protozoa are unicellular heterotrophs 2. usually reproduce asexually 3. grouped by the way they move a. some have pseudopodiacytoplasm extensions that act like false limbs b. others use cilia or flagella to move 4. Four main groups a. amoebas- shapeless, have no cell wall, use pseudopodia to move and feed, forming them around their food, can live in fresh or salt water, and usually reproduce asexually b. flagellates- have whip-like flagella for movement c. ciliates- use small hair like cilia that cover their bodies to move, can live in every type of aquatic environment (ponds, streams, oceans), paramecium is an example, usually divide through asexual reproduction d. sporozoans- produce spores, reproductive cells that form w/out fertilization and produce new organism, all are parasites that live in hosts C. Algae- plant like protists 1. use photosynthesis 2. can be single or multicellular 3. producer of oxygen & nutrients in aquatic ecosystems (food source for shellfish) 4. are not plants-lack roots, stems, & leaves 5. Types divided in 6 phyla a. Euglenoids- unicellular, aquatic *have animal and plant characteristics *most have chlorophyll & photosynthesize *can ingest food when light is absent *have 1 or more flagella to move toward light or food b. diatoms- unicellular, photosynthetic *shells made of silica *make up large component of phytoplankton (shellfish food!) *store food they make as oil instead starch, allows them to float *reproduce asexually & sexually of c. dinoflagellates- have cell walls of thick cellulose plates * mostly marine, have 2 flagella causing them to spin *also make up a large component of phytoplankton d. Red algae- mostly multicellular marine seaweeds *body is called a thallus, lacks roots & stems *use “holdfasts” to attach to rocks *red algae can live in deep water due to their photosynthetic pigments, also contain chlorophyll e. Brown algae *about 1500 species * all live in salt water in cool areas *contain chlorophyll and brown carotenoid pigment *many have air bladders that allow them to float *largest and most complex are kelp, giant kelp can grow up to 60m long f. Green algae *most diverse group, more than 7000 species *major pigment is chlorophyll *most live in freshwater *can be unicellular or multicellular *can reproduce asexually or sexually *have a complex life cycle -examples: Volvox (lives in a colony), Spirogyra (multicellular) D. Funglike protists 1. slimemolds, downy mildews, and water molds act like fungi 2. heterotrophic decomposers 3. Slime molds a. beautifully colored, live in cool, moist places, grow on rotting leaves or decaying wood 4. water molds & downy mildews a. live in water or moist areas b. some feed on dead organisms, others are plant parasites c. can look fuzzy, like a fungus, but produce flagellated reproductive cells (fungi don’t) d. downy mildew can cause disease in many plants (Great potato famine)