Protists PowerPoint
advertisement

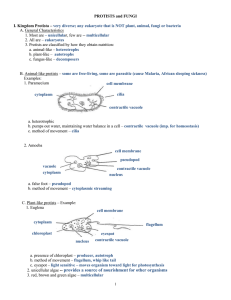
PROTISTS Chapter 2 Lesson 3 PROTISTS A. Eukaryotes that cannot be classified as animals, plants or fungi B. A diverse group Most are unicellular Some are large, simple multicellular Some are heterotrophs Some are autotrophs Some are both heterotrophic & autotrophic Some can move Some cannot move All live in moist environments ANIMAL-LIKE PROTISTS A. Like animals: Heterotrophic Most can move B. Unlike animals: Unicellular C. Sarcodines Move with pseudopods ‘false foot’ Slow moving via the cytoplasm flowing in a direction using the pseudopod and then the rest of the body follows Ex. Amoeba http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iRQTY_9Yekc D. Flagelattes Protozoans that use one or more long whiplike flagella to move Ex. Giardia http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-yIHkq9R5_c E. Ciliates Use hundreds of hairlike projections, cilia, to move and feed Ex. Paramecium http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fh_yjLppNAg F. Spore-forming parasitic protists Feed on the body fluids of their hosts Most depend on a host for transportation (ex. Mosquito) Ex. Plasmodium causes malaria PLANT-LIKE PROTISTS (ALGAE) A. Like Plants: Autotrophs that use photosynthesis & produce much of the world’s oxygen Can be multicellular B. Unlike Plants: Can be unicellular Lack true leaves, stems and roots Some can move and some are heterotrophic in addition to autotrophic C. Euglenoids Unicellular algae that can act as heterotrophs in the absence of sunlight Eyespot used to detect light Flagella that allows movement http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fI7nEWUjk3A D. Dinoflagellates Unicellular Flagella Multicolor and some glow in the dark http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EN1Yxq8KMsw E. Diatoms Unicellular Glass-like cell walls Move by oozing along a slime released from the cell wall Form diatomaceous earth used in household products like Soft Scrub and some toothpastes F. Red Algae Multicellular seaweed Can grow deep underwater because of it’s ability to absorb even a small amount of light (~260m) Nutrient rich food and is used in ice cream (makes it smoother) and hair conditioner G. Brown Algae Most seaweed The most plant-like in structure of the plant-like protists Edible and sometimes used as thickeners in puddings and other foods FUNGUS-LIKE PROTISTS A. Like Fungus: Heterotrophs Cell walls Reproduce with spores B. Unlike Fungus: Are able to move at some point in their life C. Slime Molds Brilliantly colored Unicellular or multicellular D. Water Molds & Downy Mildews Live in wet places Attack crops (ex. Irish potato famine 1845 & 1846)