Instructor`s Copy
advertisement

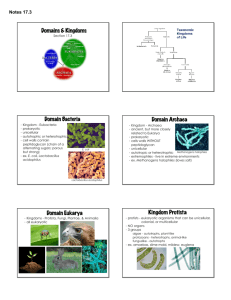
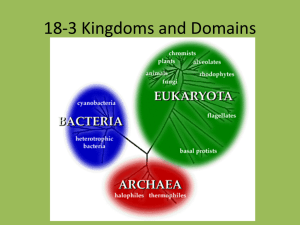
Instructor’s Copy Lab Worksheet: What Am I? Materials: Organism sheet – cut apart Procedure: Read the information on each information piece. Once you have determined which kingdom the organism belongs in, glue or tape the piece under the appropriate column. Archaebacteria Survives in volcanoes Unicellular, non-motile Data Table 1: Organisms In Each Kingdom Eubacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Lack distinct nucleus but most need oxygen Many are microscopic and produce oxygen May cause pneumonia in humans Some are autotrophs, some are heterotrophs Unicellular, non-motile Most examples reproduce by binary fission Unicellular, contain chlorophyll but no apparent leaves E. coli Amoeba Cell walls contain peptidoglycan Paramecium Animalia May cause athlete’s foot Some produce flowers Decomposer with cell wall of chitin Cell wall composed of cellulose Multicellular, heterotrophic organisms that may be parasitic but has cell walls May be monocots or dicots Some have fur All examples contain chlorophyll Tapeworm Black bread mold Shitake mushrooms Yeast Used in bread and cheese Have hyphae and mycelium Multicellular, heterotrophic organism that is made of complex systems Dog Amphibians Some have Reptiles vascular tissue Produce milk Rose Lay hardGrass shelled eggs but none fly Questions: 1. List 3 traits of bacteria. No distinct nucleus, DNA is single-stranded, no membrane-bound organelles, have a thick rigid cell wall made of peptidoglycan. 2. How can you tell the difference between archaebacteria and eubacteria? Mostly by environment, archaebacteria exist in extreme conditions. Also, cell wall lacks peptidoglycan and their cell membrane contains certain lipids that are not found in any other organism. Many cannot exist in the presence of oxygen. 3. Which two kingdoms would appear box-like under the microscope? Fungi and plantae 4. How can you tell them apart? Main difference is that plants contain chlorophyll. The cell walls of fungi contain chitin (similar to insects) which the cell walls of plants contain cellulose. 5. List 3 traits of Kingdom Protista. Eukaryotic is only set trait. Some are unicellular, some multicellular. Some need oxygen to survive, some are killed by it. Some are autotrophic, some are heterotrophic. Many are microscopic. Some reproduce sexually, some asexually. 6. List 3 traits of Kingdom Fungi. Cell walls of chitin, most are multicellular, all are heterotrophs, basic structure is a threadlike filament called a hypha. 7. List 3 traits of Kingdom Plantae. Eukaryotic cells containing chlorophyll, autotrophic. 8. List 3 traits of Kingdom Animalia. Multicellular, heterotrophs, eukaryotic cells with specialization 9. One example of Kingdom Protista has both animal and plant characteristics. What is it? Euglena 10. While most fungi are multicellular, one example is unicellular. What is it? Yeast