CONNECTIVE TISSUE
advertisement

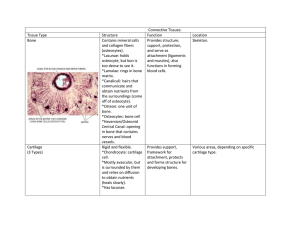
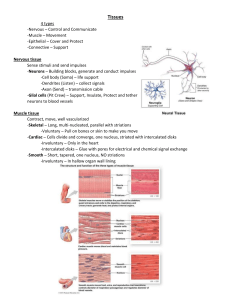
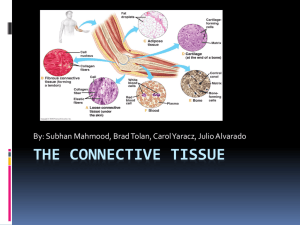
CONNECTIVE TISSUE Connects body parts Most type abundant tissue Widely Made spread up of many types of cells Common Characteristics 1. Blood supply: –Most well vascularized –Some have poor blood supply: *Tendons and ligaments – poor *Cartilages – avascular * Heal slowly 2. Extracellular Matrixnonliving substance found outside cells - produced by connective tissue - secreted to exterior Two Main Elements of the Matrix 1. Ground Substance: –Water –Adhesion proteins – glue fibers to cells –Large, charged polysaccharides (trap water as they intertwine) Less: fluid More: rock-hard 2.FIBERS • Collagen (white) • Elastic (yellow) • Reticular (fine collagen) SCURVY Loss of collagen Deficiency of Vitamin C (necessary in formation of collagen fibers) Skin sores, spongy gums, weak blood vessels, poor healing of wounds Matrix Soft packing tissue around organs Bears weight Absorb large amount of water Withstand stretching, abrasion, etc Ex: Fat: mostly cells soft Bone/Cartilage: few cells, more matrix extremely strong TYPES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE Fiber type Number of fibers in matrix BONE Osseous tissue Bone cells sitting in lacunae (cavities) Surrounded by layers of hard matrix with Ca salts and collagen fibers Protect and support body organs CARTILAGE Less hard, more flexible 1. Elastic: elasticity (ear) 2. Fibrocartilage: highly compressable (disks between vertebrae) 3. Hyaline: most widespread Collagen fibers hidden by rubbery matrix with glassy, blue-white appearance Larynx, ribs, covers ends of bones at joints Skeleton of fetus Dense Connective Tissue AKA: Dense Fibrous Tissue Collagen fibers with fibroblasts in between Stong, ropelike – TENDONS: attach skeletal muscles to bone – LIGAMENTS: connect bones to bones at joints Medial Collateral Ligament LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE Softer More cells, fewer fibers 3 types AREOLAR TISSUE Soft, pliable Cushions, protects, holds together organs Lamina propria: soft layer underlying all mucous membranes Most of matrix appears to be empty space because of loose and fluid nature Reservoir of salts and water Edema When a body region is inflamed, the areolar tissue soaks up excess fluid The area becomes puffy Phagocytes scavenge through this tissue ADIPOSE TISSUE Areolar tissue: fat cells predominate Signet ring cells: bulging nucleus looks like a ring Forms subcutaneous tissue beneath skin Insulates: temp., organs fuel Reticular Connective Tissue Delicate network of interwoven reticular fibers Forms STROMA (bed): internal supporting framework Supports free blood cells in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow) BLOOD Blood cells surrounded by blood plasma (nonliving, fluid matrix) ‘Fibers’ of blood become visible during clotting Carries nutrients, wastes, gases