Connective tissue
advertisement
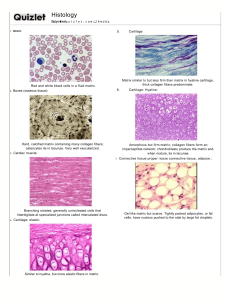
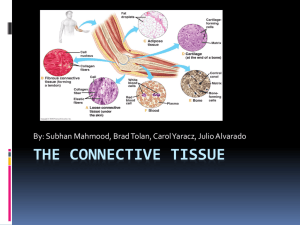
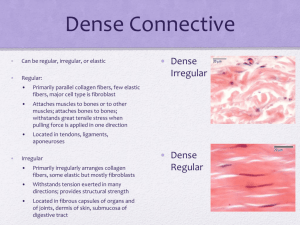
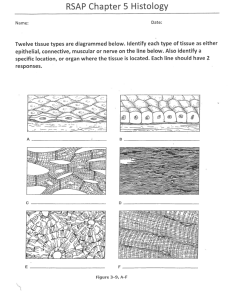
KEEPING THE BODY TOGETHER CONNECTIVE TISSUE FUNCTIONS OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE: Interconnection of tissues Support and motion Storage Cushioning and insulation Enclosing and separating Transport protection CHARACTERISTICS OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE Cells produce and maintain a matrix The cells are not usually touching – they sit within the matrix they produce The matrix allows connective tissue to perform its job WHAT IS A MATRIX? The acellular substance of a tissue The matrix is made by the cells of that tissue The matrix gives the tissue its qualities This is the cell LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE Large spaces between fibers filled with fluid or cells Examples: Areolar, adipose, and reticular ADIPOSE TISSUE (FAT) Little extracellular matrix Adipocytes filled with lipids Function: storage, thermal insulation, cushioning Found: below skin, yellow bone marrow, in spaces and crevices AREOLAR TISSUE: Has a fine network of fibers Contains fibroblasts, macrophages, and lymphocytes Function: support and nourishment Found: Around and between muscles, vessels, nerves, and organs RETICULAR TISSUE Fine network of reticular fibers irregularly arranged Spaces contain macrophages and blood cells Function: provides structure for lymphatic tissue and red bone marrow DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE - REGULAR Densely packed fibers with little space in between Fibers are mostly collagen Fibers run in one direction CONTINUED… Functions: withstand tremendous pulling forces in the direction of the fibers, stretch resistance Found: in tendons and ligaments DENSE IRREGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE Fibers run in several directions Function: provide strength in many directions, but not as strong in a single direction as DRCT Found: organ capsules, the dermis of the skin ELASTIC CONNECTIVE TISSUE Matrix made of elastic and collagen fibers Function: able to stretch and recoil Found in: walls of arteries, elastic ligaments in the spine HYALINE CARTILAGE Collagen fibers in a firm, flexible matrix Chondrocytes (the cartilage cells) sit in lacunae Function: growth of long bones, support and flexibility in trachea, bronchi, ribs, and nose Makes up the embryonic skeleton Covers articulating surfaces CONTINUED. . . . Found: ends of long bones, articular surfaces, ribs, nose, respiratory system, and the embryonic skeleton FIBROCARTILAGE Numerous collagen fibers in thick bundles Function: withstand pressure, connects structures subjected to great pressure Found: intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, knee, temporomandibular joint ELASTIC CARTILAGE Similar to hyaline cartilage but matrix also has elastic fibers Function: rigidity with flexibility, can stretch and return to original shape Found: external ear structure, epiglottis, auditory tubes BONE Hard connective tissue made by cells(osteocytes) that sit in a mineralized matrix Function: provide great strength and support, protection, movement Found: the skeleton BLOOD Liquid connective tissue Blood cells are in a fluid matrix called plasma. Function: transport, protection, temperature regulation