The connective tissue
advertisement

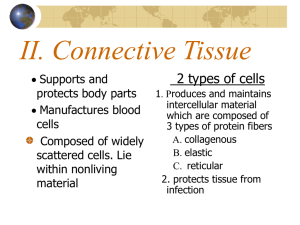
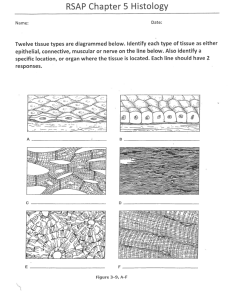
By: Subhan Mahmood, Brad Tolan, Carol Yaracz, Julio Alvarado THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE General Characteristics Connective tissue is the most abundant tissue in your body. They provide protection, support, framework, fills space, stores fat, produces blood cells, fights infection, and helps repair tissue. They are composed of more scattered cells with abundant intercellular material matrix. Most connective tissue have a good blood supply Connective tissue is made up of a ground substance (fluid, and semi-solid) and fibers Common Types of Cells Mast cells (prevents blood clots) Fibroblasts (most abundant, produces fibers) Macrophages (Phagocytic) Main types of Fibers Collagenous Fibers – are thick, made of protein collagen, major structural protein in the body, strong, flexible, not very elastic, appear in long parallel bundles, is known as white fibers. Elastic Fibers – not as strong , but very elastic (respiratory and vocal cords) Elastic Fibers and collagenous fibers Categories of Connective Loose C.T. Bone tissue Adipose Tissue (Fat) Blood Tissue Dense C.T. (Fibrous Tissue) Reticular Cartilage -Hyaline -Elastic -Fibrocartilage Loose Connective Tissue The Loose Connective Tissue binds skin to underlying organs and organs to organs. It also fills in spaces between muscles throughout the body. Dense Connective Tissue Fibrous Tissue Closely packed. It also has thick, collagenous fibers and fine network of elastic fibers. Includes tendons and ligaments. Cartilage All cartilage cells are called Chondrocytes. o Hyaline- covers end of bones and joints. o Elastic- external ear and larynx o FibrocartilageInvertebral disks Hyaline Cartilage-smooth with large nuclei. Bone Tissue Bone tissue is the osseus tissue. Rigid due to mineral salt The layers in bone tissue are haversian canals, mellae, osteocytes. Blood and Reticular The Blood tissue circulates throughout the body The Reticular tissue is scattered throughout the body Blood- identify due to platelets. Can You Identify These?