CONNECTIVE TISSUES Objectives CONNECTIVE TISSUES
advertisement
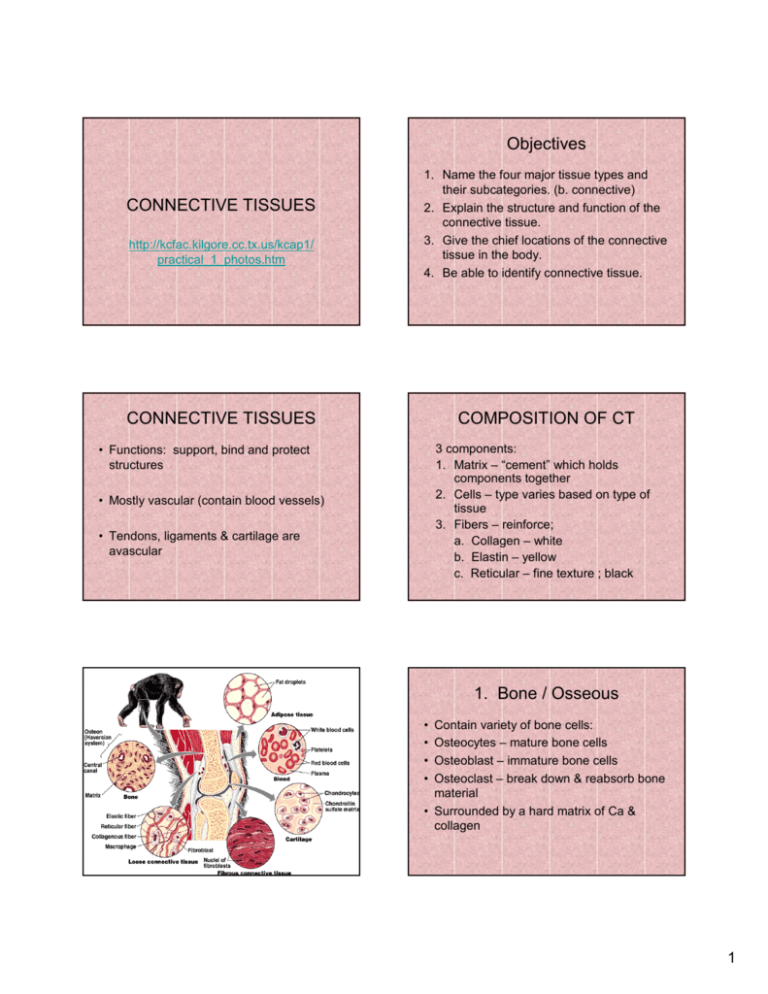
Objectives CONNECTIVE TISSUES http://kcfac.kilgore.cc.tx.us/kcap1/ practical_1_photos.htm 1. Name the four major tissue types and their subcategories. (b. connective) 2. Explain the structure and function of the connective tissue. 3. Give the chief locations of the connective tissue in the body. 4. Be able to identify connective tissue. CONNECTIVE TISSUES COMPOSITION OF CT 3 components: 1. Matrix – “cement” which holds components together 2. Cells – type varies based on type of tissue 3. Fibers – reinforce; a. Collagen – white b. Elastin – yellow c. Reticular – fine texture ; black • Functions: support, bind and protect structures • Mostly vascular (contain blood vessels) • Tendons, ligaments & cartilage are avascular 1. Bone / Osseous • • • • Contain variety of bone cells: Osteocytes – mature bone cells Osteoblast – immature bone cells Osteoclast – break down & reabsorb bone material • Surrounded by a hard matrix of Ca & collagen 1 2. Cartilage • Contain cells called chondrocytes • A. Hyaline – collagen fibers with clear glassy matrix (may have blue appearance) • Found in larynx, ribs, nose, trachea, pharynx, bronchi, embryonic skeleton • B. Elastic – found in external ear, larynx & epiglottis 3. Dense Fibrous or Connective • C. Fibrocartilage – found in intervertebral disk • • • • Collagen fibers in matrix Contains fiber forming cells called fibroblasts Two types based on arrangement of fibers A. Regular fibrous – fibers run parallel providing strength; found in tendons & ligaments • B. Irregular fibrous – fibers run nonparallel restricting movement; found enclosing organs & dermis of skin 2 4. Loose Connective • A. Areolar – few cells; collagen, elastin & reticular fibers; gel like matrix • Forms lamina propia – soft layer that underlies mucus membranes • Provides water & salts for surrounding tissues, nutrients & waste removal, wraps & cushions organs • Edema – condition in which tissues soak excess fluid • B. Adipose – gel like matrix, oil droplet displaces the nucleus creating a ring • Insulates body, protects organs & energy reserve 3 • C. Reticular – interwoven reticular fibers with reticular cells • Found in lymph nodes, spleen & bone marrow RETICULAR • D. Blood • Blood cells surrounded by liquid matrix called plasma • Fibers are proteins that are only visible when blood clots form • 3 cells: • Erythrocytes – rbc • Leukocytes – wbc • Thrombocytes – platelets • Transport oxygen, nutrients & wastes 4 5