Animal Organization and Homeostasis
advertisement

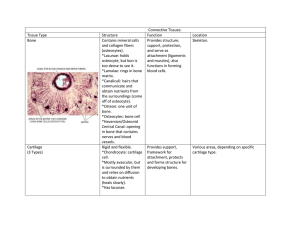
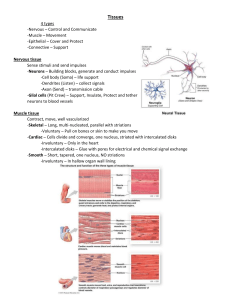
Animal Organization and Homeostasis Tissues Specialized cells of the same type that perform a common function in the body Types Epithelial Connective Muscular Nervous Epithelial tissue Covers surfaces and lines body cavities Mostly functions in protection Exposed to environment on 1 side, basement membrane on the other that anchors it to the connective tissue Named according to shape of cell Squamous (flat), cuboidal (cube) and columnar (column) Stratified (layered), pseudosratified (looks layered) Glandular epithelial Secretes a product Exocrine into a duct Endocrine into the blood stream Connective tissue Most abundant Each type has specialized cells Ground substance Protein fibers Types Fibrous connective (loose and dense) Adipose Cartilage Bone blood Fibrous connective tissue Contain fibroblast cells within a gel matrix Loose fibrous – support Adipose – energy reservoir, insulation Dense fibrous – found in tendons and ligaments, contains collagen fibers Supportive connective tissue Cartilage – cells in chambers called lacunae surrounded by a gel like matrix 3 types of cartilage (based on fibers in matrix) Hyaline – most common, fine collagen fibers Elastic - more flexible Fibrocartilage – strong collagen fibers Bone Hard matrix of inorganic salts around protein fibers Compact bone – shaft of long bones Cylindrical structures called osteons Bone cells found within lacunae Spongy bone – end of long bones Contains bony bars and plates with space between Built for strength Fluid Connective Tissues Blood – formed elements and plasma Hematopoiesis – production of blood cells, in red bone marrow Transports nutrients and oxygen to tissue fluid, distribute heat and fluid, ion and pH balance RBC’s – small, no nucleus, round WBC – larger, have a nucleus, phagocytes, produce antibodies Platelets – involved in blood clotting Lymph – in lymph vessels, absorbs excess fluid Muscular tissue Made of cells called muscle fibers Actin – thin, myosin – thick Movement and generation of heat 3 types Skeletal – voluntary, striated Smooth – visceral, involuntary, no striations Cardiac – muscles of the heart, involuntary, striated, intercalated disks Nervous tissue Contain neurons (1 trillion on average) 3 parts: axon, cell body, dendrite Functions in sensory input, integration of data, and motor output Neuroglia – support and nourish neurons Microglia - phagocyte Astroglia – provide nutrients Oligodendroglia – form myelin in brain Organs and organ systems Organ – 2 or more types of tissues working together to perform the same function Organ system – organs working together to carry out a process Skin Largest organ Functions for protection and thermoregulation Contains receptors that monitor touch, pressure, temperature and pain Epidermis Dermis subcutaneous Epidermis Stratified squamous Hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands Skin cells are pushed to surface of skin and slough off Melanocytes – cells that produce melanin, pigment, UV rays induce production (vit.D) Basal cell carcinoma and malignant melanoma are types of skin cancer Dermis and Subcutaneous Contains collagen and elastic fibers Overstretching due to fast weight gain can cause stretch marks Blood vessels and sensory receptors Subcutaneous – not true part of skin, source of energy, produces padding, overall rounded appearance Accessory organs of the skin Nails – protective covering, can be useful medically hair – begin in dermis, extend out of epidermis, dead, hardened epidermal cells Each follicle has an oil gland that when clogged, produces white heads or black heads (oxidized sebum) Glands – sweat (sudoriferous) Organ systems 2 main body cavities: Dorsal (cranial and vertebral cavity) Ventral (thoracic, abdominal and pelvic cavity) Homeostasis Maintaining and internal balance Negative feedback – keeps a variable close to a particular value ex. – body temp. Positive feedback – brings a greater change in the same direction ex. Oxytocin and birth