Other Tissues
advertisement

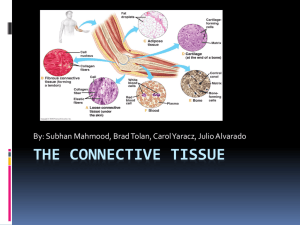
Other Tissues Connective Tissues • Connect body parts, widely distributed • Functions – Protect, Support, Bind • Characteristics – Varied blood supply – Contain an extracellular matrix Extracellular Matrix • Produced by connective tissues • Composed of – Ground substance • Water, adhesion proteins, polysaccharides • Can absorb large amounts of water – Matrix fibers • Collagen (white) fibers – strong • Elastic (yellow) fibers – stretch and recoil Connective Tissue Types • Bone – Bone cells in cavities (lacunae) – Surrounded by calcium and collagen • Cartilage – More flexible – Types • Hyaline cartilage – Collagen fibers; rubbery, blue white appearance • Fibrocartilage – Compressible, found between vertebrae • Elastic cartilage – Elastic!, external ear Connective Tissues Connective Tissues • Dense connective – Collagen fibers with fibroblasts – Tendons (muscle to bone) – Ligaments (bone to bone) – Lower layer of skin • Loose connective – Softer contains fewer fibers – Areolar tissue – cobwebby, “glue” – Adipose – fat tissue – Reticular tissue • Contains reticular cells similar to fibroblast Connective Tissue • Blood – Extracellular matrix – plasma – Invisible fibers – only visible during clotting – Transport vessel for cardiovascular system Muscle Tissue • Function: To contract to produce movement • 3 types – Skeletal • Voluntary control • Striated – Cardiac - heart • Involuntary control • Striated, contain intercalated discs – Smooth • Involuntary control • Spindle shaped, no striations • Found in walls of hollow organs Nervous Tissue • Two main functions: Irritability, conductivity • Composed of – Nerve cells (neurons) – Supporting cells – insulate, support, protect Tissue Repair • Two ways – Regeneration (replace with same type cells) – Fibrosis (replace with scar tissue) • Repair determined by – Type of tissue damaged – Severity of injury Tissue Repair • Events – Capillaries become permeable • Allow clotting proteins to get to injury • Clot stops bleeding, holds wound together – Granulation • Delicate, light pink tissue • Mainly capillaries – Regeneration • Scab detaches • New tissue exposed