Connective Tissue Chart
advertisement

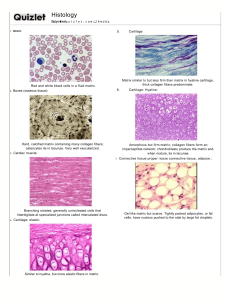
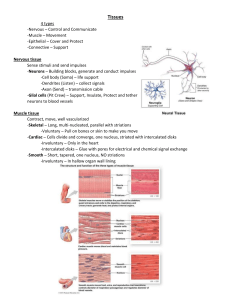
Tissue Type Bone Cartilage (3 Types) Structure Contains mineral salts and collagen fibers (osteocytes). *Lacunae: holds osteocyte, but bon is too dense to see it. *Lamalae: rings in bone matrix. *Canaliculi: hairs that communicate and obtain nutrients from the surroundings (come off of osteocyte). *Osteon: one unit of bone. *Osteocytes: bone cell *Haversion/Osteonid Central Canal: opening in bone that contains nerves and blood vessels. Rigid and flexible. *Chondrocyte: cartilage cell. *Mostly avascular, but is surrounded by them and relies on diffusion to obtain nutrients (heals slowly). *Has lacunae. Connective Tissues: Function Provides structure, support, protection, and serve as attachment (ligaments and muscles), also functions in forming blood cells. Provides support, framework for attachment, protects and forms structure for developing bones. Location Skeleton. Various areas, depending on specific cartilage type. Type 1: Hyaline Moderate amounts of collagen in matrix giving it a shiny/glass like appearance. *Most abundant type. Cushions. End of nose, ribs, ends of bones, fetal skeleton. Type 2: Elastic Flexible, contains elastic fibers. Framework. Framework of ear and larynx. Type 3: Fibrocartilage Tough, densely packed collagen fibers. Provide shock absorption (cushion). Intervertebral disks, between bones of the knee. Fibrous (2 Types) Dense, tightly packed collagenous fibers with few cells and fibroblasts. Following the same path (looks like smooth muscle but that has nuclei in every cell). Binding body parts together. Various areas depending on specific type. Binding body parts together. Outer walls of kidneys and spleen. Type 1: Regular Type 2: Irregular Not following the same path, looks “busy.” Binding body parts together. Tendons and ligaments or skin. Loose/Areolar Mainly composed of fibroblasts. Forms thin membrane between organs. Gel/fluid matrix with multiple types of fibers and cells. And has a lot of open space. Acts as a reservoir of water and salts. When a body region is inflamed, areolar tissue soaks up the excess fluid and swelling (edema). Phagocytes scavenge the area. Beneath the skin and between muscles. Adipose Form of loose connective tissue. *Mostly cellular. Stores fat in the cytoplasm. Beneath the skin (provides insulation and protects organs), beneath the muscles, around the kidneys, behind the eyeballs, in some abdominal membranes, around certain joints and on the surface of the heart. Reticular Forms network and has macrophages in it. Phagocytic. Ingest and destroy foreign particles, defend the body against infection or invasion. Lymphatic organs, lymph nodes, spleen, blood and bone marrow (associated with red blood cells). Blood (3 Types) Various shapes. *Fluid Matrix: blood plasma. *Blood cells are formed in the hollow parts of certain bones. *Hematopoietic Tissue: also called red bone marrow. *Only liquid connective tissue. Circular. Transports substances, maintains homeostasis. Blood stream. Gas/Nutrients. Blood stream. Type 1: Red Blood (Erythrocytes) Type 2: White Blood (Leukocytes) Like a pom-pom. Defense. Blood stream. Type 3: Platelets-Cellular Fragments (Thrombocytes) Like an alien. Helps defend, not as good as white blood cells. Blood stream.