Connective Tissue - Galena Park ISD Moodle
advertisement

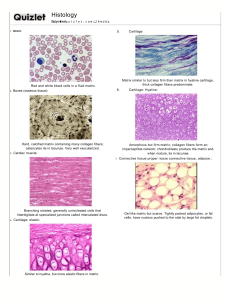
A&P Galena Park High School I. Tissue Groups Instructor: Terry E. Jones A. Definition 1. A group of closely associated cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure. B. Major Groups • 1. • 2. • 3. • 4. Epithelia – surfaces Connective – support Muscular – movement Nervous - control III. Connective Tissue A. Examples 1. Connective tissue proper (examples: fat tissue, fibrous tissue of ligaments) 2. Cartilage 3. Bone 4. Blood • B. Function: to protect, support and bind • together other tissues 1. Bones, ligaments, tendons 2. Areolar cushions; adipose insulates and is food source 3. Blood cells replenished; body tissues repaired 4. Cells separated from one another by large amount of nonliving extracellular matrix • C. Matrix 1. Nonliving material between cells 2. Produced by the cells and then extruded 3. Responsible for the strength D. Two components 1. Ground substance a. Of fluid, adhesion proteins, proteoglycans b. Liquid, semisolid, gel-like or very hard 2. Fibers: collagen, elastic or reticular • E. Loose Connective Tissue 1. Areolar – a. Gel Matrix b. 3 fibers c. Wraps and cushions organs 2. Adipose - Fat cells a. Gell matrix b. Nucleus pushed to side c. Stores fuel for organisms 3. Reticular a. Reticular fibers in loose matrix b. Supports other cell types c. Soft internal skeleton F. Dense Connective Tissue 1. Elastic and collagen fibers -tough 2. Tendons 3. Ligaments 4. Aponeuroses G. Cartilage Connective Tissue 1. Hyaline a. Collagen fibers b. Ends of long bones c. Nose, larynx d. Rib cartilage 2. Elastic a. Collagen fibers b. Similar to hyaline, but more fexible c. Ears d. Epiglottis • 3. Fibrocartilage a. Thick collagen fibers b. Absorbs shocks or compression c. Vertebral discs d. Discs in knee joint • H. Bone 1. Hard calcium matrix 2. Well supplied with blood vessels 3. Cells in a lacunae (cavity) • I. Blood 1. Matrix is liquid called plasma 2. White and red Blood cells 3. Clotting fibers and enzymes J. Membranes 1. Description a. Combination of epithelia sheets and connective tissues • 2. Types of membranes a. Cutaneous membranes 1. Skin: epidermis and dermis b. Mucous membranes, or mucosa 1. Lines every hollow internal organ that opens to the outside of the body c. Serous membranes, or serosa 1. Slippery membranes lining the pleural, pericardial and peritoneal cavities 2. The fluid formed on the surfaces is called a transudate d. Synovial membranes 1. Line joints