Geometric ISOMERS of Alkenes
advertisement

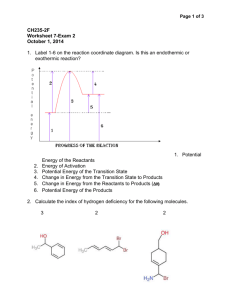
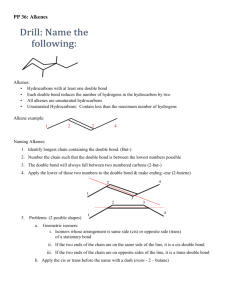
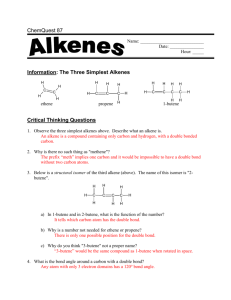
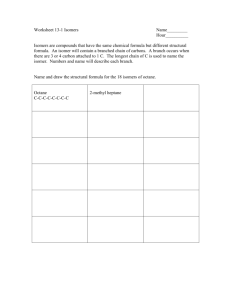
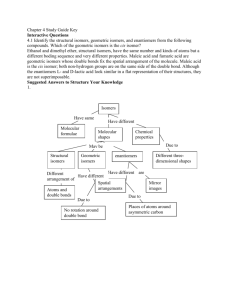
Geometric ISOMERS of Alkenes Chapter 12 Section 3 ALKENES The CARBON – CARBON double bond is rigid (no free rotation) because of the shapes of the orbitals involved in its formation Pi bond 2 p-orbital electrons lie above and below the 2 carbons Sigma bond the electrons lie in a line between the 2 carbon nuclei Rotation around the double bond is restricted because the pi bond would have to be broken to allow for rotation. THUS, THE DOUBLE BOND IS RIGID Geometric Isomers In cycloalkanes, cis/trans applied to the branches trans = on OPPOSITE sides of the ring cis = on the SAME side of the ring Geometric Isomers In alkenes, cis/trans applies to the location of the parent chain around the double bond, NOT the branches Geometric Isomers If one of the carbons of the double bond has 2 identical substituents there are NO cis/trans isomers. Example: 1,1-dichloroethene no cis/trans because both carbons have identical substituents 1,2-dichloroethene cis/trans isomers DO exist in this molecule Which exist as geometric isomers? 1-pentene 3-ethyl-3-hexene 3-methyl-2-pentene Draw these molecules. Cis-3-octene Trans-5-chloro-2-hexene Trans-2,3-dichloro-2-butene HOMEWORK 3RD EDITION: P351 #19, 23, 24, 26 4TH EDITION: P359 #21, 25, 26, 28