File
advertisement

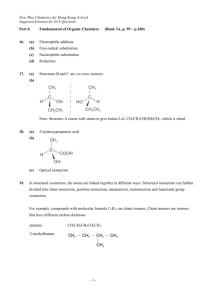
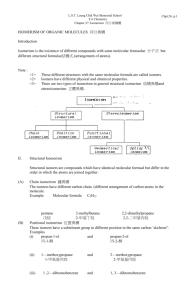
The Alkenes (1.7.3) a. state the general formula of alkenes and understand that they are unsaturated hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond which consists of a and a bond b. explain E-Z isomerism (geometric/cis-trans isomerism) in terms of restricted rotation around a C=C double bond and the nature of the substituents on the carbon atoms c. demonstrate an understanding the E-Z naming system and why it is necessary to use this when the cis- and trans- naming system breaks down Independent Learning (HW) – pp 124-128 and ALL questions therein Connector: Write the structural formulae and displayed formulae for ethene, propene and the three isomers of butene Crowe2008 H ethene C=C C2H4 H H propene C3H6 H H C=C-C H CnH2n H H H H H H H C=C C C H H H H H H H H H C C=C C H H H H H H C C=C H H H C H H H Geometric (cis-trans) isomerism cis – same side H H trans – opposite side H C=C H3 C CH3 C=C CH3 H3 C H The carbon-carbon double bond doesn't allow any rotation about it. That means that it is possible to have the CH3 groups on either end of the molecule locked either on one side of the molecule or opposite each other. cis-/trans- isomerism explained Not isomers, but a single compound The C=C double bond is rigid and so cannot rotate Isomers, two separate compounds More about cis/trans isomerism There must be two different groups on the left-hand carbon and two different groups on the right-hand one. trans-but-2-ene cis-but-2-ene But, they do not have to be the same groups. trans-1chloropropene cis-1chloropropene If blue = methyl and green = chlorine, name the four compounds here. Does 2-chloropropene exhibit cis-/trans- isomerism? No because there needs to be two different groups on each carbon! E-Z Notation for geometric isomerism For more complex molecules the cis/trans notation does not always work, e.g. How the E-Z system works •The carbon atoms at each end of the double bond are considered separately •The atom which has the higher atomic number is given the higher priority •If the two groups with the higher priorities are on the same side of the double bond, that is described as the (Z)- isomer. (The Z comes from a German word zusammen which means together.) (Zame Zide) •If the two groups with the higher priorities are on opposite sides of the double bond, then this is the (E)- isomer. (The E comes from the German entgegen which means opposite.) Name these isomers: Z-1-bromo-2-chloro-1-fluoroethene E-1-bromo-2-chloro-1-fluoroethene Name these isomers using the E-Z notation: E-1,2-dichloroethene H H Z-1,2-dichloroethene H C=C H3 C CH3 C=C CH3 Z-but-2-ene H3 C H E-but-2-ene Name these isomers using the E-Z notation: E-1-chloro-2-deuteroethene Z-1-chloro-2-deuteroethene D = deuterium, 2 1H In this case, since the atomic no. of H & D is the same, mass is used to give priority. Homework Draw the isomers of pentene (6) and name them. Use the E-Z notation for any geometric isomers. For more complicated molecules you work your way along the carbon chains, once again prioritising by atomic number Second position H Second position O Second position C So takes priority First position is the same This is a Z-isomer First position is the same So takes priority Second position =O, O is counted twice Name these compounds using cis/trans and E-Z notation Does trans = E and cis = Z? Name this compounds using cis/trans and E-Z notation: cis-2-bromobut-2ene E-2-bromobut-2ene Does trans = E and cis = Z? Not always! pent-1-ene 2-methylbut-1-ene 2-methylbut-2-ene 3-methylbut-1-ene H H C H E-pent-2-ene Z-pent-2-ene H