PP 36: Alkenes
advertisement

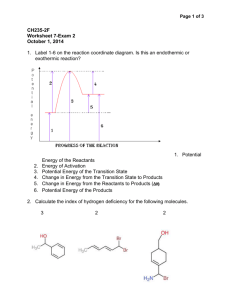
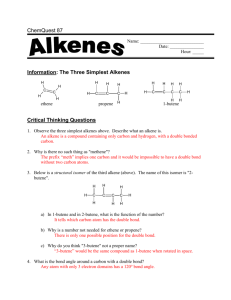
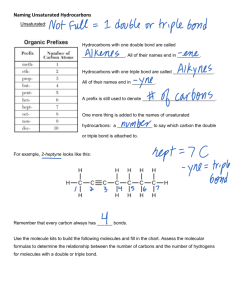
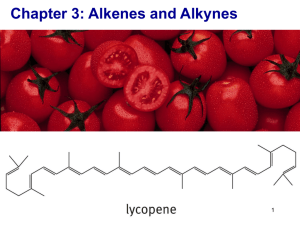
PP 36: Alkenes Alkenes: • Hydrocarbons with at least one double bond • Each double bond reduces the number of hydrogens in the hydrocarbon by two • All alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons • Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Contain less than the maximum number of hydrogens Alkene example: 1 2 3 4 Naming Alkenes: 1. Identify longest chain containing the double bond. (But-) 2. Number the chain such that the double bond is between the lowest numbers possible 3. The double bond will always fall between two numbered carbons (2-but-) 4. Apply the lower of those two numbers to the double bond & make ending -ene (2-butene) 5. Problems: (2 posible shapes) a. Geometric isomers: i. Isomers whose arrangement is same side (cis) or opposite side (trans) of a stationary bond ii. If the two ends of the chain are on the same side of the line, it is a cis-double bond iii. If the two ends of the chain are on opposite sides of the line, it is a trans-double bond b. Apply the cis or trans before the name with a dash (trans - 2 – butane) Drill: Draw the following: trans-4 - ethyl - 3,6 - dimethyl-5-cyclopentyl – 3 -octene Draw the named compound or name the drawn compound: cis-3-ethyl-4,6-dimethyl-5-cyclopropyl-2-octene Test Review: Name each of the drawn compounds & draw each of the named compounds: • • trans – 1 – cyclobutyl – 2 – methyl – 3 - hexene cis – 2 – methyl – 1 - octylcyclohexene Draw & Name isomers of: C5H10