CH 421, Post-lab 5 Name___________________________ Spring
advertisement

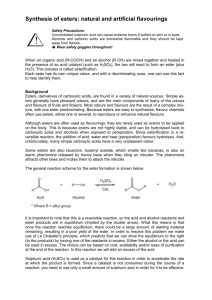
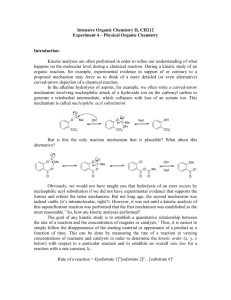
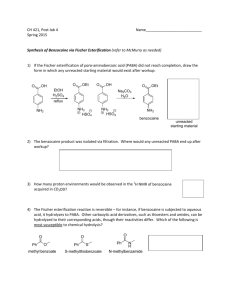
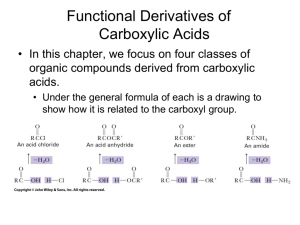
CH 421, Post‐lab 5 Name___________________________ Spring 2011 Synthesis of Benzocaine via Fischer Esterification (Pavia Exp. 44, 343‐350; refer to McMurry Chapter 21) O OH O OEt i. EtOH, H2SO4, reflux ii. Na2CO3, H2O NH2 para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) NH2 ethyl 4-aminobenzoate (benzocaine) 1) The Fischer esterification reaction requires large quantities of alcohol, which limits its synthetic utility to methyl esters, ethyl esters, and other simple esters. For more complex esters, an alternative approach is utilized. Treatment of an acid chloride with an alcohol affords an ester, as illustrated below for preparation of an intermediate towards the synthesis of Novocaine®. O O Cl O2N + HO O N O2N N+ H Cl- Outline the step‐by‐step mechanism of this reaction, using curved arrows to show the flow of electrons. Note a tetrahedral intermediate is initially formed from the nucleophilic attack of the alcohol on the acid chloride. 2) What reagent can be used to prepare an acid chloride from a carboxylic acid? 3) In the synthesis of Novocain® (procaine), the nitro group is reduced after reacting the acid chloride with the N,N‐diethylamino alcohol to form the ester. Novocain® (procaine) O Briefly explain why the following acid chloride intermediate is not used: Cl H2N 4) Arrange the following compounds according to their relative reactivity towards nucleophiles. _________________ > _________________ > _________________ > _________________ Most reactive Least reactive 5) Which would require more rigorous reaction conditions– the acidic hydrolysis of an ester or the acidic hydrolysis of an amide? (Rigorous reaction conditions would include heat and/or extended reaction times.) 6) Dipivefrine is a prodrug of epinephrine that is used in the treatment of glaucoma. In the cornea, dipevefrine is converted to the active ingredient epinephrine by the action of an esterase. Draw the products of dipivefrine ester hydrolysis. O O O OH H N esterase + H2O O epinephrine 2 equivalents 7) What general type of reaction occurs in the following catabolic transformations? Refer to McMurry for the general structures of these biomolecules as needed. a. b. c. d. e. f. Oxidation / reduction Hydration Dehydration Hydrolysis Condensation Decarboxylation 8) What general type of reaction occurs in the following anabolic transformations? Refer to McMurry for the general structures of these biomolecules as needed. a. b. c. d. e. f. Oxidation / reduction Hydration Dehydration Hydrolysis Condensation Decarboxylation 9) Draw the products of the following reactions. 10) Esters can be hydrolyzed under acidic or basic conditions. The first step in the mechanism of basic hydrolysis (saponification) is nucleophilic attack of hydroxide ion on the carbonyl carbon. With this in mind, rank methyl butanoate, isopropyl butanoate, and tert‐butyl butanoate according to their relative reactivity towards saponification, where 1 = most reactive and 3 = least reactive. ________ ________ ________