Age of Religious Wars
advertisement

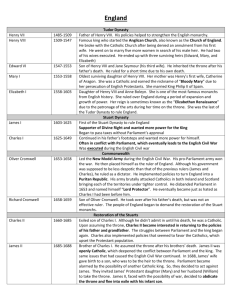
Age of Religious Wars Chapter 12 European History Key Topics War between Calvinist and Catholic in France The Spanish occupation of the Netherlands Struggle for supremacy between England and Spain The devastation of Central Europe during the 30 year war Renewed Religious Struggle Late 16-17 century described as the Age of Religious Wars because opposition of Protestants and Catholics across Europe Peace of Augsberg (1555)- A regions rule would determine its religion, However it did not recognize Non Lutheran Protestants Geneva became a refuge for persecuted protestants and an international school for protestant leaders Counter Reformation- A movement within the Rome Catholic Church that sought to revitalize the church and oppose Protestantism Baroque Art- 3 dimensional display of life and energy Politiques- Ruler who urged tolerance and moderation and compromise on religious matters French Wars of Religion Anti-Protestant Measures and the struggle for political power French Protestants are known as Huguenots. They were persecuted by the French, when King Charles of Germany / Spain captured Frances King. To pacify King Charles, France persecutes the Huguenots in the hopes of gaining the freedom of the King of France. Edict of Fontainebleau—Subjected French Protestants to the inquisition France remain hostile to the protestants until King Henry of Navarre gains the throne 3 competing fraction for the Kings (Francis II) ear in France Bourbons- power lays in the south and west Montmorency-Chatillons- controlled the center of France Guises- dominate in eastern France / Strongest power and had more influence over the king due to family connection Bourbons and Montmorency-Chatillons developed strong Huguenot sympathies Conspiracy of Amboise (1560) - Bourbons and Montmorency-Chatillons plotted to kidnap the king of France (Frances II) Appeal of Calvinism Huguenots were in important geographic areas and were heavily represented among the more powerful segments of French society. They wanted to establish sovereignty with in France. Catherine De Medicis and the Guises Catherine mother to 15 year old Frances II becomes the regent of France upon the death of her husband Henry II. On the death of Frances II her younger son Charles IX becomes king where she resides as regent. Catherine fears the power of the Guiles family and sought alliances with the Protestants. She issues the January Edict which allows protestants freedom to worship publicly outside of towns. Duke of Guise surprised a protestant congregation at Vassy Champagne and massacred the worshipers. This is the beginning of the French wars of Religion March 1562 Coligny (leader of the Huguenots) Charles IX most trusted advisor. Peace of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1570) Ended the thirty year war, the crown acknowledging the power of the Protestant nobility, granted Huguenots religious freedoms within their territory. Catherine fearing the mounting power of the other two families and protestants she cultivates the support of the Guise. The Saint Bartholomew’s Day Massacre Catherine tried to have Coligny assassinated by a bullet. Fearing the fallout from the attempt, she convinces King Charles that the Huguenots were attempting to attack Paris On Saint Bartholomew’s Day August 24, 1572, Coligny and 3000 Huguenots were massacred in Paris. With in 3days another 20,000 were executed Protestant Resistance Theory John Knox- wrote First Blast of the Trumpet against the Terrible Regiment of Women he declared removal of a heathen tyrant was permissible Francois Hotman- wrote Franco-Gallia Humanist argument that representative Estate General held more authority then the French king Theodore Beza- wrote On the Right of Magistrates over their Subjects permissible for lower authorities to overthrow tyrannical rulers Philippe du Plessis Mornay- Defense of Liberty against Tyrants Princes, Nobles and magistrates are guardians and to take up arms against tyranny in other land The Rise to Power of Henry Navarre Henry III sought the middle ground and gained support from a growing body of neutral Catholics and Huguenots Peace of Beaulieu May 1576- granted the Huguenots almost complete religious and civil freedom. It was later recanted because of political pressure of the Catholic League. Both religious orders pick up arms. Henry Navarre led the Protestant army. (Henry III brotherin-law) Day of the Barricades –Henry III surprise attack on the Catholic League (Spain Supported) and failed. Henry then assassinated the Duke and Cardinal of Guise. Reprisal from the League was fierce causing Henry III to join forces with Henry Navarre. Henry III was killed; Henry IV (Navarre) is the next successor to the throne. Now there is a Protestant as king, the League wants France to be Catholic but politically weak so Spain sends in troops to help achieve this goal in hopes of putting his daughter on the throne. The French rallied behind their king disbanding the League and outing the Spanish. Henry IV turns Catholic. Ending the war of religion in France Edict of Nantes Proclaimed a formal religious settlement it recognized minor religions in an official Catholic country Treaty of Vervins ended hostility between France and Spain Imperial Spain and the Reign of Philip II Gold Silver and bullion were being imported from Spain’s colonies in the New World. The increased wealth and population in large cities in Europe triggered inflation. Their were fewer jobs, less food, wages stagnated and greater coinage in circulation while prices increased The Revolt in the NetherlandsAntoine Perrenot (Cardinal Granvelle) hoped to break the local autonomy of the Netherlands providences and establish a centralized royal government directed from Madrid, and religious conformity to Catholic. Granvelle proceeded to reorganize the Netherlands. William of Nassau (Prince of Orange) & Count of Egmont organized the Dutch nobility in opposition, which had Granvelle removed from office The CompromiseA solemn pledge to resist the decrees of Trent and the Inquisition. Margaret (Regent of Spain) spurred the protesters. Which leads them to call for aid and rebel against Spain, however the nobility does not support the rebellion. Duke of Alba is sent to the Netherlands to gain control back. He had several thousand suspected heretics publicly executed. He then taxed the people of Netherlands to pay for the suppressing of the revolt. Pacification of GhentNovember 4 1576 Spanish mercenaries ran amok in Antwerp killing 7000 people in the streets known as the Spanish fury. Catholic regions and Protestant regions in the Netherlands unified to oppose Spain, became known as the Pacification of Gent November 8 1576 Perpetual Edict- provided for removal of all Spanish troops from the Netherlands within 20 days. Netherlands IndependenceKing of Spain Phillip II declared William of Orange an outlaw. December 1580 William of Orange publicly denounced Phillip as a Heathen and tyrant and should not be obeyed known as the Apology. Peace of Westphalia in 1648 – Netherlands is fully recognized England and Spain 1553-1603 Family Tree- Henry VIII Mary 3rd Queen Elizabeth 4th Queen Edward 1st king Jane Grey (granddaughter to Henry) Mary I – reign lasted 5 years Edward VI died and tried to have Lady Jane Grey to ascend to the throne. However Mary Tudor was the rightful heir. Grey lasted 9 days then beheaded. Mary marries Prince Philip II of Spain. Mary had Parliament repeal the Protestant laws. Mary decreed all of England Catholic and burned Protestant leaders at the stake Mary dies 1558 Elizabeth I – takes throne 1558 Daughter of Henry and half sister to Mary. Advisor William Cecil. Passed laws for religious toleration Act of Supremacy 1559- Repealing all anti-Protestant legislation of Mary Tudor Phillip II seeks marriage with Elizabeth. Mary Stuart Queen of Scots seeks England throne her claim Elizabeth is illegitimate and she is the granddaughter to Henry the VIII sister Margaret. Deterioration of Relation with Spain Spanish Duke of Alb 1547 marched troops into the Netherlands; England sees this as a threat due its close proximity to England. Elizabeth allows pirating of Spanish vessels. Mary Queen of Scots Elizabeth executes Mary Queen of Scotts (second cousin) for plotting against the crown. Mary’s husband is killed by her lover, who is acquitted, and then marries Mary. This causes outrage from her people. Mary surrenders her throne to her one year old son James VI, who later becomes Elizabeth’s heir to throne. The pope authorize Spain to invade England for the killing of Mary who was their hope to turn England Catholic The Armand May 30 1587 a 130 ships with 25,000 sailors sent to invade England. Spain wanted the ships to dock in France before continuing the invasion. France prohibit the ships from leaving and a fog roles in around the channel giving England the advantage and wins. Thirty Year War Preconditions for War Germany = Holly Roman Empire (pg 408 has map of various religions) Germany consists of 360 autonomous entities. Each had its own tolls, taxes, coins and religion, making it difficult to travel and do business Four Periods of WarBohemian (1618-1625) Danish (1625-1629) Swedish (1630-1635) Swedish-French (1635-1648) Bohemian Period- (pg 410 for map) Ferdinand ascends to the throne and wants to return the region to Catholicism. He revokes the religious freedoms of the Bohemian Protestants. In reaction the Protestant nobility in Prague throws Ferdinand 3 regents out the window known as “defenestration of Prague” However they did not die, landed on manure which cushioned their fall. Ferdinand was managed to subdue the Protestants and re-Catholicize Bohemian Danish Period- (1625-1629) Lutheran King Christian IV of Demark picks up the Protestant banner and invades Germany and loses. Ferdinand then attacks Demark and breaks Protestant resistance. Issues the Edict of Restitution in 1629- Calvinism is illegal and orders the return of all church lands acquired by the Lutherans. This causes fear among all Protestants. The Swedish Periods (1630-1635) Gustavus Adolohus king of a unified Lutheran nation, bankrolled by France who wishes to keep the Habsburg armies tied down in Germany. Adolhus won several battles due to a lighter army and better weapons. However Adolus is killed on the battlefield. The Peace of Prague in 1635 majority of the Protestants states reached a compromise with Ferdinand except for the Swedes which plunged them into the fourth war. The Swedish-French Period (1635-1648) The French join the war in 1635. The war dragged on for 13 years with Spainish, French and Swedish soldiers looting Germany. About 1/3 of the German population died as a direct result of the war Treaty of Westphalia- (pg 412 map) The treaty of Westphalia 1648 brought all hostilities within the Holy Roman Empire to an end. It ends the Edict of Restitution and reasserts the Peace of Augsburg, which allows each ruler to determine its religion. German princes becomes supreme over their principalities.